Objective of the ‘O’ Level Course
The objective of the course is to equip a student with necessary skills as per following job role.
- User Interface (UI) Designer
- Web Designer
- Web Publication Assistant
- Office Automation Assistant v. IoT Application Integrator
About The Revised Syllabus The fourth revised version of DOEACC ‘O’ Level (IT) syllabus came into effect in January 2010 examinations. Since then, much advancement has been observed in the area of Information Technology. The need of industry has also changed with the availability of new and advanced technologies and tools. With the advancement in technologies, the software development practices have also changed. This also has led to change in job profile. Different job roles require different skills. Moreover, the digital initiatives taken by Government have also changed the way the business is taking place these days. These factors have led to bringing the revision in syllabus of DOEACC ‘O’ Level (IT) course.
This document presents the fifth revised version of ‘O’ Level syllabus under DOEACC Scheme which becomes effective for teaching with immediate effect. The syllabus of ‘O’ Level course is designed to enhance the skills of students so as to enable them to solve problems using Information Technology (IT) tools. The self-learning approach is built into the syllabus enabling the learners to update themselves on the changing technologies in their area of work. The syllabus has been designed to meet the skills required for various IT job roles. 2. NIELIT National Institute of Electronics and Information Technology, NIELIT, (Erstwhile DOEACC Society) is an autonomous scientific society of the Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology, Government of India.
The Society is registered under the Societies Registration Act, 1860. NIELIT was set up to carry out Human Resource Development and related activities in the area of Information, Electronics & Communications Technology (IECT). NIELIT is engaged both in Formal & Non-Formal Education in the areas of IECT besides development of industry oriented quality education and training programmes in the state-of-the-art areas. NIELIT has endeavored to establish standards to be the country’s premier institution for Examination and Certification in the field of IECT. It is also one of the National Examination Body, which accredits institutes/organizations for conducting courses in IT and Electronics in the non-formal sector.
NIELIT has acquired very good expertise in IT training through its wide repertoire of courses. These courses are as under.
- ‘O’ Level –NSQF aligned course at Level 4
- ‘A’ Level -NSQF aligned course at Level 5
- ‘B’ Level - NSQF aligned course at Level 7
- ‘C’ Level - NSQF aligned course at Level 8
Digital Literacy Courses
- ACC (Awareness in Computer Concepts)
- BCC (Basic Computer Course)
- CCC (Course on Computer Concept) –NSQF aligned at Level 3
- CCC+ (Course on Computer Concept Plus)
- ECC (Expert Computer Course)
Objective of Scheme The objective of the Scheme is to generate skilled manpower in the area of Information Technology (IT) and Electronics at the national level by utilizing the facilities and infrastructure available with the institutions/organizations in the non-formal sector. NIELIT is managed and administered by a Governing Council which consists of eminent academicians and professionals from IT and Electronics industries. Minister for Electronics& Information Technology, Government of India, is the Chairman of the Governing Council.
M2-R5.1 Web Designing & Publishing Theory : 48 hrs. Practical : 72 hrs. Total : 120 hrs.
NIELIT Course Page click here for Different
Courses
Syllabus of Web Designing and Publishing (M2-R5.1)
Introduction to Module This module is designed to start web designing, irrespective of knowledge currently the students have in this area. The businesses, nowadays, are heavily relying on web based applications. The purpose of this module is to provide skill to students in designing layouts of web sites. By the end of this module, students will be able to describe the structure and functionality of the World Wide Web, create web pages using a combination of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript and Angular JS. The students will also learn how to design and integrate multimedia objects in web site. Further, the student will learn how web sites are published.
Objective After completing the module, the student will be able to:
- Design and create effective web pages
- Integrate graphics in web pages
- Integrate various tools and techniques like HTML, CSS, JavaScript, Angular JS etc.
- Design and edit images using tools
- Embed the images in web pages
Duration 120 Hours - (Theory: 48hrs + Practical: 72 hrs)
Detailed - Syllabus Revision 5.1 for ‘O’ Level (IT) Under DOEACC Scheme
(i) Introduction to Web Design Introduction of Internet, WWW, Website, Working of Websites, Webpages, Front End, Back End, Client and Server Scripting Languages, Responsive Web Designing, Types of Websites (Static and Dynamic Websites).
(ii) Editors Downloading free Editors like Notepad++, Sublime Text Editor, making use of Editors, File creation and editing, saving.
(iii) HTML Basics HTML: Introduction, Basic Structure of HTML, Head Section and Elements of Head Section, Formatting Tags: Bold, Italic, Underline, Strikethrough, Div,Pre Tag Anchor links and Named Anchors Image Tag, Paragraphs, Comments, Tables: Attributes (Border, Cellpadding, Cellspacing , height , width), TR, TH, TD, Rowspan, Colspan Lists : Ordered List , Unordered List , Definition List, Forms, Form Elements, Input types, Input Attributes, Text Input Text Area, Dropdown, Radio buttons , Check boxes, Submit and Reset Buttons Frames: Frameset, nested Frames. HTML 5 Introduction, HTML5 New Elements: Section, Nav, Article, Aside, Audio Tag, Video Tag, HTML5 Form Validations: Require Attribute, Pattern Attribute, Autofocus Attribute, email, number type, date type, Range type, HTML embed multimedia, HTML Layout, HTML Iframe
(iv) CSS Introduction to CSS, Types of CSS, CSS Selectors: Universal Selector, ID selector, Tag Selector, Class Selector, Sub Selector, Attribute Selector, Group Selector, CSS Properties: Back Ground properties, Block Properties, Box properties, List properties, Border Properties, Positioning Properties, CSS Lists CSS Tables, CSS Menu Design CSS Image Gallery,
(v) CSS Framework Web Site Development using W3.CSS Framework, W3.CSS Intro, W3.CSS Colors, W3.CSS Containers, W3.CSS Panels, W3. CSS Borders, W3.CSS Fonts, W3.CSS Text, W3.CSS Tables, W3.CSS List, W3.CSS Images, W3.CSS Grid
(vi) JavaScript and Angular JS Introduction to Client Side Scripting Language, Variables in Java Script, Operators in JS, Conditions Statements, JS Popup Boxes, JS Events, Basic Form Validations in JavaScript. Introduction to Angular JS: Expressions, Modules and Directives. (vii) Photo Editor Features of Photo Editing: Tools: Selection Tools, Paint Tools, Transform Tools, Text Tool, Layers, Brightness/ Contrast, Improve Colors and tone, Filters.
(viii) Web Publishing and Browsing Overview, SGML (Standard Generalized Markup Language), Web hosting Basics, Documents Interchange Standards, Components of Web Publishing, Document management, Web Page Design Considerations and Principles, Search and Meta Search Engines, WWW, Browser, HTTP, Publishing Tools.
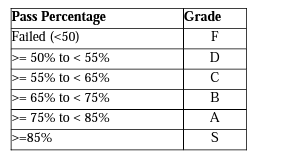
Gradation Structure
Reference Books/Study Material
1. HTML5, Black Book, Kagent Learning Solution Inc, 2014 2. Mastering HTML, CSS &JavaScript Web Publishing by Lemay Laura, BPB publications 3. HTML & CSS: The Complete Reference by Thomas Powell 4. Web Design, McGraw –hill 5. Learning Angular JS by Brad Dayley.
The Internet is the backbone of the Web, the technical infrastructure that makes the Web possible. At its most basic, the Internet is a large network of computers which communicate all together.
The various technologies that support the Internet have evolved over time, but the way it works hasn't changed that much: Internet is a way to connect computers all together and ensure that, whatever happens, they find a way to stay connected.
The term web server can refer to hardware or software, or both of them working together.
On the hardware side, a web server is a computer that stores web server software and a website's component files (for example, HTML documents, images, CSS stylesheets, and JavaScript files). A web server connects to the Internet and supports physical data interchange with other devices connected to the web.
On the software side, a web server includes several parts that control how web users access hosted files. At a minimum, this is an HTTP server. An HTTP server is software that understands URLs (web addresses) and HTTP (the protocol your browser uses to view webpages). An HTTP server can be accessed through the domain names of the websites it stores, and it delivers the content of these hosted websites to the end user's device.
Getting started with the web
Getting started with the web is a concise series introducing you to the practicalities of web development. You'll set up the tools you need to construct a simple webpage and publish your own simple code.
The story of your first website
It's a lot of work to create a professional website, so if you're new to web development, we encourage you to start small, but it's not hard to make your own simple website online, so we'll start there.
Let's begin our journey!
Installing basic software
When it comes to tools for building a website, there's a lot to pick from. If you're just starting, you might be confused by the array of code editors, frameworks, and testing tools out there. In this article, we will show you step-by-step how to install the software you need to begin some basic web development.
What will your website look like?
Before you start writing the code for your website, you should plan it first. What information are you showcasing? What fonts and colors are you using? Here we'll outline a simple method that you can follow to plan out your site's content and design.
Dealing with files
A website consists of many files: text content, code, stylesheets, media content, and so on. When you're building a website, you need to assemble these files into a sensible structure and make sure they can talk to one another. This article explains how to set up a sensible file structure for your website and what issues you should be aware of.
HTML basics
HyperText Markup Language (HTML) is the code that you use to structure your web content and give it meaning and purpose. For example, is my content a set of paragraphs or a list of bullet points? Do I have images inserted on my page? Do I have a data table? Without overwhelming you, this article will provide enough information to make you familiar with HTML.
CSS basics
Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) is the code that you use to style your website. For example, do you want the text to be black or red? Where should content be drawn on the screen? What background images and colors should be used to decorate your website? In this article, we'll take you through what you need to get started.
JavaScript basics
JavaScript is the programming language that you use to add interactive features to your website. Some examples could be games, things that happen when buttons are pressed or data is entered in forms, dynamic styling effects, animation, and much more. In this article, we'll give you an idea of what is possible with this exciting language, and how to get started.
Publishing your sample code
Once you have finished writing the code and organizing the files that make up your website, you need to put it all online so people can find it.
How the web works
When you access your website, a lot of complicated things happen in the background that you may not know about. Here we will outline what happens when you view a webpage on your computer.
Know why "web developer" is a great career to choose.
(i) Introduction to Web Design Introduction of Internet, WWW, Website, Working of Websites, Webpages, Front End, Back End, Client and Server Scripting Languages, Responsive Web Designing, Types of Websites (Static and Dynamic Websites).
What exactly a framework is ?
- A framework is developed by the developers for the developers.
- It is a structure that can build software on
- Framework is used to build a software or application.
- Framework serves as the foundation .
- It is a programming language specific.
- It is suited for different types of tasks.
- you could pour the foundation and frame the house yourself.
- A Framework is built / tested and optimized by several experienced developers and software language and programmer.
- It is robust, versatile and efficient also.
- Framework is supporting structure around which something can be built around.
- Framework = tool of organizing information
- A framework provides set of tools in programming on which to build well structured, reliable software and system.
- It speed up and simplify web development process.
- A framework is a scheme of work generally used by programmers to perform software development. Using a framework allows you to streamline development processes as it avoids having to write code repetitively, ensures good practices and code consistency.
- A framework is therefore a set of tools and modules that can be reused for various projects. One of the most well-known and used frameworks is the Microsoft .NET Framework for websites.
- Other examples are bootstrap, w3CSS etc.

Advantages of Frameworks
Among the advantages of using a framework for software development we distinguish:
The programmer saves time since he already has the skeleton on which to develop an application.
It facilitates collaborative developments, by leaving programming standards defined.
Being widespread, it is easier to find tools, modules and information to use it.
It provides greater security, having a large part of the potential vulnerabilities resolved.
There is usually a community behind it, a set of developers who can help answer queries.
Framework Examples
Here are some of the most well-known frameworks:
- Net is Microsoft Framework and one of the most used.
- Symphony: PHP free software project.
- Zend Framework: Open source framework for developing web applications and with PHP web services.
- Laravel. One of the easiest open source frameworks to assimilate for PHP.
- Django: open source web development framework written in Python.
- Ruby on Rails: Open source web application framework written in the Ruby programming language.
- Angular: open source framework developed in TypeScript and maintained by Google.

Introduction to Web Design
Types of web site.
- Types of Websites That You Can Make
- Business Website
- Ecommerce Website
- Blog
- Entertainment Website
- News Website
- Nonprofit/Organization Website
- Membership Website
- Portfolio
- Personal Website
- Forum
- Knowledge base
- Portfolio website
- Event website
- Personal website
- Informational website
- Online forum
Differences Between a Theme and a Templates
Theme and template are two words we frequently encounter in web development. Unfortunately, people often conflate the two and use them interchangeably.
But are theme and template synonyms? Is there any tangible difference between them? Let’s find out.
Here, we look deep into what themes and templates exactly mean. So you will not be confused about when to use which.
What is a Theme?
A theme is what gives structure to your whole website. It is the backbone of any website. A theme defines how your website looks in its entirety. Every component that naturally comes to mind when you think of a website is guided by the theme.
Theme is the blueprint of the functionality of a website. Every aspect of a website, including page layouts, font style, margins, indentation, sidebar positioning, color palette, and typography, is controlled by a theme.
In short, choosing a theme for your website means choosing a comprehensive design.
What is a Template?
A template is a single-page layout, whereas a theme is the total design of a website. In WordPress and similar systems, a template is a theme component.
Contrary to this, in some design systems, a template stands for the whole website design. So, one should be aware of the design system when referring to templates and themes. Otherwise, it would lead to more confusion.
A theme may contain multiple templates for different elements like header, footer, blog post design, landing page design, etc. Templates make a website stand out from others by adding unique custom layouts for each page.
Theme Vs. Template Major Differences
Theme
Defines the comprehensive design of a website
A website can only have a single theme
Controls the typography and functionality of the entire website
Websites functions through a single theme
Template
Refers to the single-page layout
A website may have multiple templates
Customizes the website with different types of templates
Installation of template without a theme is not possible
Web designing is the process of creating and designing websites. It involves planning, conceptualizing, and arranging the layout, colors, graphics, and content of a website. Web designers use various tools and programming languages like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to create visually appealing and user-friendly websites. They also consider factors such as user experience, accessibility, and search engine optimization to ensure that the website meets the needs of its target audience.
Web development is the process of creating and maintaining websites. It involves various tasks such as designing the layout, writing code, and implementing functionality to make the website interactive. Web developers use programming languages like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to build websites that can be accessed and used by people on the internet. They also work with web servers, databases, and other technologies to ensure the website runs smoothly and securely. Is there anything specific you would like to know about web development?
The relationship between web designing and web development is quite interconnected. Web designing refers to the process of creating the visual layout and aesthetics of a website. It involves designing the user interface, selecting color schemes, typography, and creating a visually appealing website.
On the other hand, web development involves the technical aspects of building a website. It includes writing code, programming, and implementing the design into a functional website. Web developers use programming languages like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to bring the design to life and make the website interactive.
Web design and web development are two closely related fields that are essential for creating and maintaining websites. However, they are not the same thing.
Web design is the process of creating the visual elements of a website, such as the layout, colors, fonts, and images. Web designers use their creativity and technical skills to create websites that are visually appealing and user-friendly.
Web development is the process of creating the functional elements of a website, such as the code that allows users to interact with the website. Web developers use programming languages such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to create websites that work as intended.
In some cases, a single person may be responsible for both web design and web development. However, it is more common for these two roles to be filled by separate individuals or teams.
Here is a table that summarizes the key differences between web design and web development:
Web design Web development
Concerned with the visual appearance of a website Concerned with the functionality of a website
Uses software such as Adobe Photoshop and Illustrator Uses programming languages such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript
Requires creativity and an eye for design Requires technical skills and knowledge of programming languages
May be responsible for creating wireframes, mockups, and prototypes May be responsible for coding the website, testing it, and deploying it
If you are interested in a career in web development or web design, there are many resources available to help you learn the skills you need. There are online courses, tutorials, and bootcamps that can teach you the basics of web design and web development. You can also find mentorship programs and networking opportunities to help you connect with other professionals in the field.
No matter which path you choose, a career in web design or web development can be rewarding and challenging. With the right skills and experience, you can create websites that are both visually appealing and functional.
In summary, web designing focuses on the visual aspects and user experience, while web development focuses on the technical implementation and functionality of the website. Both are essential for creating a successful and user-friendly website.
About Chat GPT-3.5
A highly conversational go-to model for explanations, translations, and creative writing.
==================================
In the world of networking, computers do not represent by names like humans do, they represent by numbers because that is how computers and other similar devices talk and identify with each other over a network, which is by using numbers such as IP addresses.
An application called a DNS resolver is in charge of translating domain names into IP addresses. The DNS resolver contacts a DNS server to seek the IP address associated with a domain name when a user types it into their web browser.
DNS Server: A DNS server is a piece of software that keeps track of domain names and IP addresses. It answers with the appropriate IP address to requests from DNS resolvers.
The initial point of contact in the DNS system is a DNS root server. It offers details on the DNS servers in charge of top-level domains (TLDs), including.com,.org, and.net.
TLD Server: A TLD server is a DNS server that is in charge of keeping track of data on domain names that fall under a certain top-level domain, such as.com or.org.
What is a DNS server?
The Domain Name System (DNS) is the phonebook of the Internet. When users type domain names such as ‘google.com’ or ‘nytimes.com’ into web browsers, DNS is responsible for finding the correct IP address for those sites. Browsers then use those addresses to communicate with origin servers or CDN edge servers to access website information. This all happens thanks to DNS servers: machines dedicated to answering DNS queries.
How do DNS servers resolve a DNS query?
In a typical DNS query without any caching, there are four servers that work together to deliver an IP address to the client: recursive resolvers, root nameservers, TLD nameservers, and authoritative nameservers.
The DNS recursor (also referred to as the DNS resolver) is a server that receives the query from the DNS client, and then interacts with other DNS servers to hunt down the correct IP. Once the resolver receives the request from the client, the resolver then actually behaves as a client itself, querying the other three types of DNS servers in search of the right IP.
First the resolver queries the root nameserver. The root server is the first step in translating (resolving) human-readable domain names into IP addresses. The root server then responds to the resolver with the address of a top-level domain (TLD) DNS server (such as .com or .net) that stores the information for its domains.
Next the resolver queries the TLD server. The TLD server responds with the IP address of the domain’s authoritative nameserver. The recursor then queries the authoritative nameserver, which will respond with the IP address of the origin server.
The resolver will finally pass the origin server IP address back to the client. Using this IP address, the client can then initiate a query directly to the origin server, and the origin server will respond by sending website data that can be interpreted and displayed by the web browser.
Key Questions
Question 1 What do you mean by website?
Solution: The website is a collection of interlinked web pages, with a common domain name. The website can be made by any individual, group, or company. All the websites together constitute the world wide web.
Question 2: What is the worldwide web? When it was discovered?
Solution: Timothy Berners-Lee has invented the world wide web in the year 1989. Basically, the world wide web is an interconnected system of all public web pages which can be enabled through an internet connection.
Question 3: What are the languages need for Web development?
Solution: For developing a website, a developer should know many languages, like HTML, CSS, JavaScript etc. But, initially, a developer needs to command over HTML, which is the basic requirement to develop a website.
Question 4: What is an e-commerce website? Give an example of it.
Solution: The E-commerce website is a place for online shopping where a person can buy or sell a product. Amazon, Flipkart and Olx are some of the examples of an E-commerce website.
Question 5: Write any 4 types of websites with examples.
Solution: There are many websites present on the internet. Let’s discuss some of them:
The blog is a website where people share information, their ideas and views. It is a place where you can express your vision and your thoughts to the world. Earlier, Blogs were used as a journal, but now they are becoming one of the important mass communication tools where people get to know about new things. WordPress and Google blogger are one of the famous blogging sites where you can write articles.
The informational website provides information on various topics. For example, Wikipedia is an information website where you can get information about everything.
Social media websites are the most popular websites that enable the user to share their personal information, pictures, video opinions and opinion in real-time. Facebook and Twitter are examples of social media websites.
Educational websites include websites of colleges and schools and institutions. The new normal has changed the structure of educational institutions. Nowadays, people are learning through online classes and the demands of educational websites are also growing. As people want to learn more than their college and schools. So there are platforms like Coursera, GeeksforGeeks where people are learning more than their college and school.
Editors
RESOURCES :
Understand working of different editors. Explore more on Code Editors here
O Level Project Submission
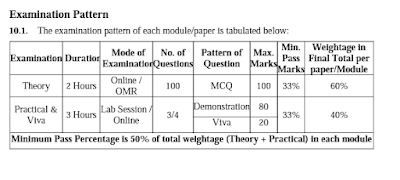
At 'O' Level, there is one Project. Candidate is required to do Project individually and no grouping is allowed. Project would be approximately 100 man-hours and carries a total of 100 marks (80% for the Project evaluation and 20% for the Viva-Voce). Student is required to obtain at least 50% marks in total to qualify for the Project.
Eligibility Criteria for submission of 'O' Level Project
'O' Level student can submit Project only after clearing 2 papers of the 'O' Level Course.
How to submit 'O Level Project Report
The student will submit his/her Project Report in the prescribed format along with the requisite fee. The Project Report should include:
a) One Hardcopy of Project Report.
b) Softcopy of Project Report.
c) The Project Report may be about 50 pages (excluding coding).
The following suggested guidelines may be followed in preparing the final Project Report:
1. Good quality white executive bond paper A4 size should be used for typing and duplication. Care should be taken to avoid smudging while duplicating the copies.
2. Page specification (written paper and source code)
Left margin - 3.0 cms.
Right margin - 3.0 cms.
Top margin - 2.7 cms.
Bottom margin - 2.7 cms.
O Level Project Submission
At 'O' Level, there is one Project. No marks are assigned. Candidate is expected to carry out a Project under the guidance of your guide successfully and submit a certificate in the prescribed format duly endorsed by the head of Accredited Institute where the Candidate has undergone training or the Organization where the Candidate has to make the Project.
In case of direct candidates with graduation, the candidate may make a project under a Guide or under the supervision of a person with NIELIT A level with adequate experience of minimum five years’ experience (or) NIELIT B level / MCA (or) equivalent/higher qualification without any experience.
Prescribed format for 'O' Level Project is given at Annexure - I
Project Fees at 'O' Level
A fee of Rs.100/- (Rupees One Hundred only) should be done through NEFT/RTGS/Net Banking Payment only and no payment through Demand Draft will be accepted.
Details of the NIELIT Bank Account for Online transaction are given below:
Name of the Bank: Bank of India
Branch: CGO Complex Branch, New Delhi-110003
Name of the Account: NIELIT
Current A/C No.: 604820100000012
IFSC Code: BKID0006048
MICR Code: 110013052
Contact Details
In case of any other query, please feel free to contact us at projects@nielit.gov.in or 011-25308300 Extn no.524, 532
Project ‘O’ Level (IT) courses has a project as an important component. The project is carried out by the student under guidance and support of faculty and management of Institute / Organization where the student is undergoing training. It is felt that such a project provides an opportunity to the student to apply his / her knowledge and skills to real life problems (including oral and written communication skills). The project should be given utmost importance and priority both by the students as well as institution faculty / management in respect of its identification, planning and implementation. 8.1. Objective of the Project Syllabus Revision 5.1 for ‘O’ Level (IT) Under DOEACC Scheme Page No. 6 The objective of the project is to give the students additional hands-on experience in solving a real life problem by applying knowledge and skills gained on completion of theory papers in a course at a given Level. It provides an opportunity to students to develop written and communication skills. Project also helps the students to realize the importance of resource and time management, ownership of task towards deliverables, innovation and efficiency in task management apart from presentation skills. It also provides a good opportunity for students to build, enhance and sustain high levels of professional conduct and performance and evolves a problem solver frame of mind in the students. It is also felt that taking up the project by a student prepares him/her for a job in industry and elsewhere. 8.2. Project Submission The student undergoing course ‘O’ level (IT) course has to submit project in order to be ‘O’ Level certified. The project should be original and of real life value. The project should not be copy of existing material from any other source. The Learners (Students) are expected to carry out a project successfully and submit the project certificate in the prescribed format from the head of the institute running the accredited course or the organization of which the learner is an employee. Proforma of the Project Completion Certificate is given on next page.
Sample
Project is Here just click here














No comments:
Post a Comment
If you have any query or doubt, please let me know. I will try my level best to resolve the same at earliest.