डिजिटल लिटरेसी मतलब एक कदम उन्नति की तरफ
Now let's know What exactly is Digital Literacy :) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=U4wLvLQ5AFI
About Digital Literacy
The goal of Digital Literacy is to bring Digital Transformation
Introduction to Digital Literacy: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8o96ey4jCgE
Hope you have grasped the idea of Digital Literacy now!!...
Know the Importance of Digital Literacy: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3ePSrhlWCYE
So What exactly is digital literacy?
So, developing technical skills is crucial. But digital literacy doesn’t just mean IT Infect, digital literacy is separate from computer literacy. It requires critical thinking skills, an awareness of the necessary standards of behavior expected in online environments, and an understanding of the shared social issues created by digital technologies.
Or
alternatively:
Digital literacy = Digital tool knowledge + critical thinking + social engagement.
Let's recap another aspect of what exactly is Digital Literacy :)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_LElWqXi7Ag
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NlfY-c7RxL8
Literacies of 21 Century
Digital Literacy is also known as Practical Computer skills or computer literacy or digital literacy or IT literacy or ICT [Internet and Communication technology] Literacy or technology literacy or Information literacy Or media literacy or communication literacy or visual literacy. All these are also known as sub-discipline of digital literacy. So basically Digital Literacy is an extension term for information technology (IT)
Digital literacy empower people to solve their problems by learning the Literacies of 21 Century
New literacies of this era is the collection of some abilities, which are required to create and communicate meanings, develop oneself, and participate in a speedy changing society.

Information literacy is a set of abilities requiring individuals to "recognize when information is needed and have the ability to locate, evaluate, and use effectively the needed information." 1 Information literacy also is increasingly important in the contemporary environment of rapid technological change .
Every organization is standing in the queue to become ONLINE first.
These technologies empower everyone to perform best in their field especially in the education field.
Digital Literacy may contribute effectively in the completion of academic projects, students can use online resources in educational field in productive way.
Internet = cyber space
Basic operation of Computer
Computer
A computer is an electronic device, operating under the control of instructions stored in its own memory that can accept data (input), process the data according to specified rules, produce information (output), and store the information for future use.
Functionalities of a computer
Any digital computer carries out five functions in gross terms:
· Takes data as inputs
· Stores the data / Instructions in its memory
· Processes the data and covert it into useful information
· Generates output
· Controls all the above 4 steps
Computer Components
Any kind of computers consists of HARDWARE AND SOFTWARE
Hardware:
Computer hardware is the collection of physical elements that constitutes a computer system. Computer hardware refers to the physical parts or components of a computer such as the monitor, mouse, keyboard, computer data storage, hard drive disk (HDD), system unit (graphic cards, sound cards, memory, motherboard and chips), etc. all of which are physical objects that can be touched.
Input Devices
Input device is any peripheral (piece of computer hardware equipment to provide data and control signals to an information processing system such as a computer or other information appliance. Input device Translate data from form that humans understand to one that the computer can work with. Most common are keyboard and mouse.
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
A CPU is brain of a computer. It is responsible for all functions and processes. Regarding computing power, the CPU is the most important element of a computer system.
The CPU is comprised of three main parts:
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU):
Executes all arithmetic and logical operations. Arithmetic calculations like as addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. Logical operation like compare numbers, letters, or special characters.
Control Unit (CU): controls and co-ordinates computer components.
1. Read the code for the next instruction to be executed.
2. Increment the program counter so it points to the next instruction.
3. Read whatever data the instruction requires from cells in memory.
4. Provide the necessary data to an ALU or register.
5. If the instruction requires an ALU or specialized hardware to complete, instruct the hardware to perform the requested operation
Registers: Stores the data that is to be executed next, "very fast storage area".
Primary Memory: -
1. RAM: Random Access Memory (RAM) is a memory scheme within the computer system responsible for storing data on a temporary basis, so that it can be promptly accessed by the processor as and when needed. It is volatile in nature, which means that data will be erased once supply to the storage device is turned off. RAM stores data randomly and the processor accesses these data randomly from the RAM storage. RAM is considered "random access" because you can access any memory cell directly if you know the row and column that intersect at that cell.
2. ROM (Read Only Memory): ROM is a permanent form of storage. ROM stays active regardless of whether power supply to it is turned on or off. ROM devices do not allow data stored on them to be modified.
Secondary Memory: - Stores data and programs permanently: its retained after the power is turned off
1. Hard drive (HD): A hard disk is part of a unit, often called a "disk drive," "hard drive," or "hard disk drive," that store and provides relatively quick access to large amounts of data on an electromagnetically charged surface or set of surfaces.
2. Optical Disk: an optical disc drive (ODD) is a disk drive that uses laser light as part of the process of reading or writing data to or from optical discs. Some drives can only read from discs, but recent drives are commonly both readers and recorders, also called burners or writers. Compact discs, DVDs, and Blu-ray discs are common types of optical media which can be read and recorded by such drives. Optical drive is the generic name; drives are usually described as "CD" "DVD", or "Bluray", followed by "drive", "writer", etc. There are three main types of optical media: CD, DVD, and Blu-ray disc. CDs can store up to 700 megabytes (MB) of data and DVDs can store up to 8.4 GB of data. Blu-ray discs, which are the newest type of optical media, can store up to 50 GB of data. This storage capacity is a clear advantage over the floppy disk storage media (a magnetic media), which only has a capacity of 1.44 MB.
3. Flash Disk A storage module made of flash memory chips. A Flash disks have no mechanical platters or access arms, but the term "disk" is used because the data are accessed as if they were on a hard drive. The disk storage structure is emulated.
Output devices an output device is any piece of computer hardware equipment used to communicate the results of data processing carried out by an information processing system (such as a computer) which converts the electronically generated information into human readable form.
Note Basic types of monitors are a.Cathode Ray Tube (CRT). B. Liquid Crystal Displays (LCD). c.light-emitting diode (LED). Printer types: 1-Laser Printer. 2-Ink Jet Printer. 3-Dot Matrix Printer
Software
Software is a generic term for organized collections of computer data and instructions, often broken into two major categories: system software that provides the basic nontask-specific functions of the computer, and application software which is used by users to accomplish specific tasks.
Software Types
A. System software is responsible for controlling, integrating, and managing the individual hardware components of a computer system so that other software and the users of the system see it as a functional unit without having to be concerned with the low-level details such as transferring data from memory to disk, or rendering text onto a display. Generally, system software consists of an operating system and some fundamental utilities such as disk formatters, file managers, display managers, text editors, user authentication (login) and management tools, and networking and device control software.
B. Application software is used to accomplish specific tasks other than just running the computer system. Application software may consist of a single program, such as an image viewer; a small collection of programs (often called a software package) that work closely together to accomplish a task, such as a spreadsheet or text processing system; a larger collection (often called a software suite) of related but independent programs and packages that have a common user interface or shared data format, such as Microsoft Office, which consists of closely integrated word processor, spreadsheet, database, etc.; or a software system, such as a database management system, which is a collection of fundamental programs that may provide some service to a variety of other independent applications.
Unit of Measurements
Storage measurements: The basic unit used in computer data storage is called a bit (binary digit). Computers use these little bits, which are composed of ones and zeros, to do things and talk to other computers. All your files, for instance, are kept in the computer as binary files and translated into words and pictures by the software (which is also ones and zeros). This two number system, is called a “binary number system” since it has only two numbers in it. The decimal number system in contrast has ten unique digits, zero through nine.
Size example
· 1 bit - answer to an yes/no question
· 1 byte - a number from 0 to 255.
· 90 bytes: enough to store a typical line of text from a book.
· 4 KB: about one page of text.
· 120 KB: the text of a typical pocket book.
· 3 MB - a three minute song (128k bitrate)
· 650-900 MB - an CD-ROM
· 1 GB -114 minutes of uncompressed CD-quality audio at 1.4 Mbit/s
· 8-16 GB - size of a normal flash drive
Speed measurement:
The speed of Central Processing Unit (CPU) is measured by Hertz (Hz), Which represent a CPU cycle. The speed of CPU is known as Computer Speed.
Computers classification
Computers can be generally classified by size and power as follows, though there is Considerable overlap:
· Personal computer: A small, single-user computer based on a microprocessor. In addition to the microprocessor, a personal computer has a keyboard for entering data, a monitor for displaying information, and a storage device for saving data.
· workstation : A powerful, single-user computer. A workstation is like a personal computer, but it has a more powerful microprocessor and a higher-quality monitor.
· minicomputer : A multi-user computer capable of supporting from 10 to hundreds of users simultaneously.
· mainframe : A powerful multi-user computer capable of supporting many hundreds or thousands of users simultaneously.
· supercomputer : An extremely fast computer that can perform hundreds of millions of instructions per second.
Data, Information and Knowledge
Data: Facts and figures which relay something specific, but which are not organized in any way and which provide no further information regarding patterns, context, etc. So data means "unstructured facts and figures that have the least impact on the typical manager.
" Information: For data to become information, it must be contextualized, categorized, calculated and condensed. Information thus paints a bigger picture; it is data with relevance and purpose. It may convey a trend in the environment, or perhaps indicate a pattern of sales for a given period of time. Essentially information is found "in answers to questions that begin with such words as who, what, where, when, and how many".
Knowledge: Knowledge is closely linked to doing and implies know-how and understanding. The knowledge possessed by each individual is a product of his experience, and encompasses the norms by which he evaluates new inputs from his surroundings.
The content of the human mind can be classified into four categories:
1. Data: symbols
2. Information: data that are processed to be useful; provides answers to "who", "what", "where", and "when" questions
3. Knowledge: application of data and information; answers "how" questions
4. Wisdom: evaluated understanding. We need to understand that processing data produced Information and process Information produces Knowledge and so on
Nowadays "Digital literacy " has become the "Personal Required Skills" as it includes:
1. Functional Skills
Students & even Teachers should have enough grounding in digital technologies to be able to efficiently navigate them during class time. This understanding should be deep enough that when new technologies emerge, teachers have the fluency to puzzle out how to navigate them on their own or in conjunction with colleagues.
2. Search Skills
Students should know how to navigate search engines in order to return relevant, respectable and safe results that represent a broad spectrum of perspectives.
3. Evaluating Sources
Teachers & Students both should be able to determine a reputable website from one that is untrustworthy, biased, dangerous or outdated. They should be able to guide students toward attaining these same skills.
4. Critical Thinking
At a deeper level, teachers should be able to think critically about the sources and digital tools that they find and rely on so they can teach students how to think critically.
5. Creativity
Students &Teachers should have a deep enough understanding of available digital tools to propose and guide students through creative projects that stretch these tools to the limits of what they can do.
6. Communication
Teachers & Students should be able to communicate on digital technologies in a manner that is appropriate for each platform.
7. Cultural Contexts
Both students and Teachers should have sensitivity to the varying cultural contexts that students bring both to the classroom and to digital technologies. They should know how to use technology in order to differentiate their approaches.
8. Safety
Students & Trainers should understand digital and online safety. They should know how to teach the habits of a digital citizen and look out for their students online in a manner that still gives students independence.
9. Insight on Technology Purchases
Learners should be able to provide feedback on district technology purchases, guiding administrators wherever possible to match purchased technologies with classroom needs.
10. Flexibility
Since technology demands change so rapidly, digitally literate teachers or students will be able to adjust to these changes.
11. Knowledge of Chat Platforms
As tools like Mystery Skype External link and Google Hangouts External link make their way into the classroom, knowing how to use such technologies is key, in that they open up a world of access and knowledge. On these platforms, students can talk to experts around the world, take a virtual field trip, or even find an online mentor. Teacher literacy with these tools is becoming essential.
12. Knowledge of PLN Platforms
Having a Personal Learning Network (PLN) is key to learning, growing, and staying on top of the latest and greatest digital and pedagogical innovations. Twitter is particularly popular among teachers. Learning how to navigate this platform will open teachers up to a world of information and perspectives both within and outside of their subject areas.
13. Understanding of Data
Educational technology is often powerful because of the precise data that it can provide on each student’s performance. Understanding this data will help digitally literate teachers differentiate their instruction and intervene with students who are struggling.
14. Collaboration
A digitally literate teacher will use digital tools to connect and collaborate with other teachers, whether on their team or across the world, as they develop professionally and coordinate on projects.
Extra Credit
Multi-Platform Competency
It’s great when a teacher comes to school with a deep familiarity of a particular platform, app or technology, especially if that teacher or even a student is willing to promote that technology to other teachers /students. It is not, however, essential, as a truly digitally literate teacher will be able to adapt to other technologies beyond their immediate expertise.
Coding Skills
Teachers who can code or work in HTML will have a leg up when it comes to developing their own classroom technology, as well as in teaching students directly about how to do these things. However, these skills are not necessary as long as teachers are literate enough to be able to talk about them in a cogent manner.
What is digital learning? How it is changing the traditional education system? what are its advantages and disadvantages? Digital education new normal - future of learning.
To get the answer of this question let's understand from this visuals or video.
4c of Digital literacy for future jobs
- Communication
- Collaboration
- Creativity
- Critical thinking


Adaptable, flexible, resilience and agile people are in demand by the industry experts
The digital revolution has started now!!..
Digital skills = Digital Literacy
Qs How to Develop Digital Literacy and why to develop it?
Job Market is looking for graduates with Digital skills or digital literacy
Digital Landscape is expanding now!.
Digital literacy is the future skills or future of India as India badal raha hai!.. Digital India
Make in India
Digital literacy teaching methods expand on Print Literacy with the following tools:
- Cloud computing
- · Courseware
- · Multimedia slides
- · Game-based learning
- · Educational video
- · Audio learning
- · Digital production
- Interacting on digital devices
- Combining virtual and physical worlds
Conventional and digital literacy go hand-in-hand in the classroom, enriching your students’ creative thinking and integrating them into today’s digital world.
In classrooms with very diverse learners, how can educators take into account each individual student’s needs and help all children develop to their full potential? Adaptive teaching is a promising approach, and digital tools offer a great opportunity to tailor instruction to each learner and free up teachers’ time for individual support. However, this approach can only be truly successful if it is available to all children, providing a more equitable educational environment for everyone.
Play Video (3130) Using digital tools to transform the classroom - YouTube
Building Communication and Literacy Skills with Digital Media
It’s important that educators expand their ideas about literacy. Children in grades K-12 adapt to technology naturally, making it the best time to teach Internet technology skills. It’s the time for them to create relationships between the written and visual word for better communication with others.
Communicating through pen and ink is a lot different from communicating in the technological, visual world where children need to be aware of appearance, gestures, and the tone in which they speak. These qualities don’t matter in printed material, but they’re essential skills that student need to learn for effective communication today.
Traditional literacy is all about learning nouns, verbs, sentences, grammar, and reading and writing text. By taking a broader look at digital literacy, implementing technology in the classroom greatly enhances the learning experience beyond conventional literacy. This interactive visual media deepens understanding, thinking, and interpreting content, elevating your students beyond the confines of structured literacy.
Digital Literacy Goes Beyond Reading and Writing
Advances in technology provide digital resources for education curriculums, which significantly contribute to digital literacy learning. For example, when students have digital tools available for writing assignments, they enjoy creating multimedia presentations that enhance their writing skills. The following digital tools help bring your students’ writing to life:
Insert relevant videos
Insert images
Receive instant feedback with chat features
Ability to search and attain facts instantly
Edit spelling and grammar themselves
Access to more experts and data
Revise work without having to rewrite the whole paper
5 Ways Digital Literacy Makes Learning More Effective
Traditional classroom settings restrict the time and space of students’ learning capabilities. When you offer them technology tools, it opens the door to the whole universe. They can learn anywhere, anytime and about anything. It’s a way to extend learning beyond the walls of the classroom to help encourage a lifetime of learning and sharing knowledge.
1. Take learning everywhere
When your students learn how to use digital media, they can utilize this skill everywhere. Technology is all around them. For example, at home they probably have smart devices like mobile phones, tablets, computers, and other smart devices. Your students can take their knowledge with them, using their digital literacy skills for profound learning outside the classroom.
2. Interact with peers
Another benefit of harnessing new technology in the classroom, especially in older children is the interpersonal computing they can do. When students work on their assignments using cloud environments, they can interact with each other, reviewing, offering encouragement, and making suggestions. This not only helps motivate students to perform better, but it builds collaboration and negotiation skills that they can use throughout their entire lives.
3.Digital literacy and e-safety
While it has the potential to deliver immense value, our online world also comes with inherent risks, particularly for children. The truth is, while younger generations are being labelled as digital natives when it comes to safety, they are often no more literate than their parents.
Digital platforms make children vulnerable to criminals and bullies, especially during a time of lockdown and social isolation. They can cause students to compare their existence to the often-fabricated online lives of others, inciting feelings of inadequacy, detachment, isolation, and even the development of mental health issues. They can also leave pupils open to misinformation, manipulation, and fake news.
Here are some practical examples to be introduced into Digital Literacy:
Teach students about online safetyTo teach pupils about staying safe online, and the threats of internet grooming, sexting, cyberbullying and identity theft, the NSPCC has collated a number of lesson plans and online guidance. This includes advice on the importance of protecting personal information, including passwords and the distribution of photographs. Students should also be taught never to give out personal data as part of e-safety education.
Introduce students to “fake news”Fake news isn’t just for politicians; it has now crept into the classroom. So teachers must teach their students that not everything we see and read online is true. Here are some top tips to help you fight fake news in your classroom.
Challenge in advertising
There is clear evidence that advertising and promotions have an impact on children. For example, junk food TV ads have been shown to make children hungry and tempted. So it’s no wonder that the UK Committee of Advertising Practice’s non-broadcast marketing code states that communications addressed to, targeted directly at, or featuring children (those under 16) must contain nothing that is likely to result in their physical, mental or moral harm. But protecting children from online advertisements is harder, especially when it is not always obvious what constitutes an ad.
To teach children how to spot online advertisements, teachers can ask students to explore the pervasiveness of online ads in their own lives. Once they have examined the commercials aimed at them – and identified what they are trying to sell and how – they can create new ads with positive, age-appropriate messages.
FG Work
MODULE -1
- Which social media platforms do you use? and why ?
- How much time do you spend on social media on a daily basis?
- Which is your favourite social media platform? Why?
- Have you deleted any post or had a fight with someone on social media? Why did that happen?
- Do you agree that we should use social media with caution?
- What do you like about platforms such as YouTube, Amazon Prime, Hotstar, etc?
- Come up with Pros and Cons of using various OTT platforms such as Netflix, HotStar and Amazon Prime
- Find out the difference between:
- a. Correct news and fake news.
- b. Original profile and fake profile
- How you will be using internet for fulfilling their personal requirements.
Today we will start with the module Using Internet for Professional Requirements in the subject of Digital Literacy.
In this chapter, we will be studying about the ways we can use internet for fulfilling our
various Professional Requirements.
a. Thank you email
b. Offer email
c. Job application email
d. Promotional email
e. Request email
f. Informing email
- Your purpose of writing the email.
- The job position you are interested in.
- Your name and contact detail.
- Your educational qualifications, training and work experience.
- Your job application cover letter as an attachment. If you are writing the cover letter in the email body, then you do not require to add it as an attachment.
- Your CV as an attachment.
- Any other additional documents that the employer mentioned as a requirement in the job advertisement.
Template For A Job Application Email
You can refer to the following email template when composing your job application:
To: [Recipient email]
Subject: Your name - Application for [Job title]
Salutation: Dear Mr./Mrs./Ms. [name of recipient]
Email body:
In the first paragraph, mention the job position you want to apply for and the place where you saw the job advertisement. Give a brief introduction of yourself and mention why you are interested in the job.
In the second paragraph, mention your educational qualifications, skills and work experience. Elaborate on why these make you a suitable candidate for the available work position.
In the third paragraph, list any work links that you want the recipient to review. You can also mention the attachments that you are sending along with the email.
In the closing paragraph, inform the recipient that you hope to hear from them and discuss things further. Thank them for their time and attention. Sign off with a closing salutation like "Kind Regards" or "Sincerely". Type your name or insert your signature below and include your phone number.
With the advancement in technology, it is no longer required for job seekers to travel and visit different organisations in person to apply for the jobs. They can do the same online by just mailing their resumes and that too to multiple organisations of their choice either though online job portals or through the career section on a company’s website.
But before applying for a Job online, one must have a Resume and Cover Letter ready.
a. Chronological
b. Functional
c. Combinational
- This type of resume helps employers quickly understand the value of your most recent and relevant work experiences.
- As employers may only spend a few seconds review each resume they receive, prioritising the most recent information helps ensure your experience and relevant information gets seen by the employer.
- Several years of experience in one career path
- Worked for several employers or clients in one industry
- Minimal or no gaps between jobs
- If you are a recent graduate or fresher with little or no professional experience, you might consider using a functional or combination resume.
- A functional resume format is also useful if you have been out of work for a significant amount of time. If you are changing positions or industries, a combination resume might be a better fit.
- In this case, a resume that puts more emphasis on your transferable skills and abilities may be more beneficial to potential employers.
- Clean and prepare treatment rooms for proper hygiene and sanitation
- Prepare patient for dental treatment to maintain appointments
- Answer common patient questions to help them relax during treatment
- Educate patients about dental procedures, treatments and issues
- Communicate with patients about referral system to increase appointments by 25%
- Dental Assistant | May 2019–October 2021
- Organised client schedules to optimise appointments and fit two more appointments in daily on average
- Received patients upon arrival and helped them prepare for appointments
- Handled client billing and paperwork efficiently to support dentists
- You’re a recent graduate with no employment experience.
- You’re making a career change.
- You have a long history of gaps between jobs.
- You are returning to the workforce.
- You have limited work experience.
- Cover gaps in their employment
- Bloat their skills.
- Hide their lack of experience.
- This is easy to do because the main focus of a functional resume is on skills rather than career history.
- Highlight your work experience, include measurable results, and provide context.
- “I definitely want to see everything laid out in context,” said the expert.
- Recruiters want to have a better idea of the context of every skill and accomplishment. And the functional resume doesn’t offer this.
a. Application
b. Referral
c. Interest
d. Networking
e. Value Proposition
a. Industries
b. Designation
c. Departments
d. Qualification
e. Degrees
f. Location
1. Email or Electronic mail is an electronic form of the traditional postal mail that allows
people to exchange messages and files with others over a network.
2. A resume or CV is a document that provides summary about a person’s work experience,
education, skills and achievements to a prospective employer.
3. A cover letter is written specifically for the job one is applying for and used to highlight
and elaborate the skills and areas of expertise of a job seeker.
4. If we compare Email with traditional postal service, instead of using pen and paper
emails make use of software program to write a message while the network server
becomes a postal employee and delivers the message to the recipient.
5. An email should be professional, organized, clear, to the point and also grammatically
correc
1. Creating an Email The steps of creating an email are as follows:
1. Selecting a service: There are various email providers such as Gmail, Yahoo,
Outlook, etc. You can choose one based on your requirements.
2. Visiting the website: Visit the website of the service provider of your choice.
3. Sign Up: Choose the option of creating a new account and fill the necessary details
such as phone number, username, passwords, etc.
2. Managing email messages
Some of the tips to manage email messages are as follows:
1. Set aside time to read and respond to email.
2. Take action immediately.
3. Organize an inbox with labels, folders and categories.
4. Unsubscribe from unwanted promotional emails.
3. Do’s and Don’ts of a Cover letter
DOs
Be clear and concise
Keep paragraphs short and direct
Choose a professional font
Check spelling and grammar
DON'Ts
Don’t put the whole resume.
No need to mention of other job applications.
Don’t go beyond one page
Don’t exaggerate.
4. Security Tips while applying for online jobs
Be selective: Apply only through those job portals which have a good privacy policy.
Background check: Have a background check of the position and the company
before applying.
Stay aware: Stay aware of the kind of scams which happen related to Jobs.
Don’t Pay: Never transfer money to someone account. No reputed company will ask
you to pay for a Job position.
5. Tips for Skype Interviews
Look at the camera not at the screen: This helps to make an eye contact with the person
Surroundings: Ensure the background is clutter free and the place is quiet.
Dressing: Treat Skype interview just as the in-person interviews and dress accordingly.
Lights, camera, and sound: Make sure lighting is good, camera is proper and sound is good.
Close Other Programs: Close all the other programs to avoid distractions during the
interview.
Get in touch with old colleagues
Use your profile as a resume
Find and apply to jobs
Connect with new professionals
Participate in groups
Q. 5. Answer the following questions in 6-7 lines.
1.) Components of an email
An email message consists of the following general components:
Headers: The header contains information concerning the sender and recipients.
Subject: Subject is a description of the topic of the message. A subject line could be
something like "Call for Interview", "Materials Required for Pathology Set-up”, etc.
Sender (From): This is the email address of the sender's from whom the mail is
received.
Date and time received (On): This section displays the date and time when the
message was received.
Reply-to: This is the email address that will become the recipient of your reply if you
click the Reply button.
Recipient (To :): First/last name of email recipient.
Recipient email address: The email address of the recipient.
Attachments: Attachment includes the files such as images, documents, etc. attached to the message. Emails can contain text, pictures, data files, audio flies, video clips, etc.
The body of a message contains text that is the actual content and describes the purpose of
sending the message. The message body also may include signatures or automatically
generated text that is inserted by the sender's email system.
2.) 6 key components to structure emails
The 6 key components to structure Emails are as follows:
Subject Line: The subject line highlights the importance of an Email along with the key
information within the message.
Subject line should be clear, concise and meaningful.
It should be related to the main message of the mail.
One word Subject line such as Help, Urgent should be avoided.
Greeting: The way you greet makes a first impression on the recipients.
Intro: The intro of the message should provide the recipient summarized information about
the context of the message.
Intro should be clear, concise and meaningful.
Restrict the intro to one or two sentences.
Detail: The detailed part of the message provides information about the issue or the situation.
Use bullet points to highlight different points.
Keep the tone professional and respectful.
Mention about the attachments, if any.
Action: This is the component where you state exactly what you are looking to get, from
whom and by when.
Your call of action should be well defined and specific.
Ensure the who, the what and the when are correct.
Sign-Off: The Sign-off is the part where you provide a courteous "thank you" for assistance
and provide required contact information.
Use phrases and words which are formal and convey respect.
Use signature lines that contain contact information.
3.) Email etiquettes
Some of the email etiquettes to be followed are as follows:
Use simple and clear subject lines
Avoid subject lines that are in all caps, all lower case or include URLs.
Answer all questions, and pre-empt further questions.
Use proper spelling, grammar & punctuation
Use Proper Salutations
Keep the message short and to the point
Do not attach unnecessary files.
Use proper structure & layout.
Do not overuse the high priority option.
Do not write in CAPITALS
Avoid using shortcuts for words, emoticons, jargons or slangs in the message
Ensure you are sending the messages to the right person only.
Include signature to include your and your company name
4.) Parts of a resume
Personal detail should include the name and contact details. Generally, personal details
should be placed in the following order:
Name
Address
Phone Number
Website or digital portfolio link
LinkedIn Profile
Career Objective or Summary:
A career objective is generally placed after the personal details. A career objective should be
a short sentence and should focus on how will you use your skills and what will you do.
Education:
This part should include details of the educational qualifications. Ideally, the most recent
educational experience should be placed first. In this, the name of the institutions,
specialisations and graduation dates must be included. Any special awards and other
educational achievements can also be included here.
In this section, list your most recent jobs including the title of your position, name and location of organisation, and dates of employment. Further under each job, you can give a brief overview of your role, responsibilities and achievements, weaving in the skills required.
Internships and volunteer work can also be mentioned here.
Additional Information:
You may also create headings such as ‘Skills’, ‘Strengths’ or ‘Interests’ and list informationn that would be relevant to the job you’re applying for. It is a good practice to include information illustrating your proficiency in languages, computer programs or medical knowledge here.
5.) Do’s of a resume
DOs
Customize: Tailor your resume specific to the requirement of the job highlighting the qualifications and expertise matching to that job.
Tech skills: It is vital to accurately summarize your proficiency level with the use of
technology and software.
Achievements: It is always good to highlight your achievements either from the
previous job or college life.
Accomplishments: Include a brief list of any special recognition and awards you've
received.
Proofread: Proofread and proofread your document multiple times to remove any
possible typos or grammatical errors.
Update: Keep your resume updated by including the latest accomplishments or
experience or skills learned.
6.) Don’ts of a resume
Personal Details: Never put personal information such as photo, height, religion, etc.
on the resume.
False Information: Stay honest in all of your job application materials.
Format: Don’t use a fancy or a crazy resume format.
Reasons for leaving Jobs: Though interviewer may ask you about this in person,
there is no need to include this information on the resume.
Salary information. Do not mention about your past salary or salary expectations
anywhere in the resume.
Long Resume: Don’t make your resume long; limit it to 1 to at most 2 pages.
Personal Information:
Begin your cover letter with your contact information. Generally, information details should
be placed in the following order:
Name
Current home address
Contact Person's Information:
Here the name of the Hiring Manger, along with the title, company name and company
address should be mentioned.
Salutation:
Salutation should be appropriate.
Opening Paragraph:
Here the information about how you learned about the position should be included.
Middle Paragraph:
This paragraph gives a summary of your background and skills which make you an ideal
candidate for the particular position.
Last Paragraph:
Use this to describe your other skills for the job which gives you an edge over others.
Contact Information and Closing
At the end of the letter talk about your availability for the job, where you can be contacted, and when you are going to contact the hiring person for an appointment to discuss your application. Thank the person to whom you are writing for his/her time and consideration of your application.
The steps involved in applying for Job through the various Job portals are as follows:
1. Creating an account: You need to create an account by providing details such as
contact number, email id, etc.
2. Filtering jobs: You can filter jobs based on various categories such as:
Qualification
Designation
Area of interest
Work Experience
Location
Company name
Industry name
Salary range
3. Uploading Resume and cover letter: When you find a job of your liking, you need to
submit your updated resume and cover letter.
4. Apply: The last step is clicking the Apply button.
------------------------------------------------------------ TISS – SVE -------------------------------------------------
References:
Do-It(2018) Key Elements of a Cover Letter [Online] Available at:
https://www.washington.edu/doit/key-elements-cover-letter
[Accessed: 25th June 2018]
Novoresume (2018) How to Write a Professional Resume - 2018 Guide [Online]
Available at:
https://novoresume.com/career-blog/how-to-write-a-resume-guide
[Accessed: 25th June 2018]
Microsoft (2018) What is Skype Interviews and how do use it? [Online] Available at:
https://support.skype.com/en/faq/FA34780/what-is-skype-interviews-and-how-do-use-it
[Accessed: 25th June 2018]
Koru (2018) 9 Things You Need to Prepare for a Skype Interview [Online] Available at:
https://novoresume.com/career-blog/how-to-write-a-resume-guide
[Accessed: 25th June 2018]
Rice D (2018) 8 Best Job Portals You Must Check Out [INDIA] [Online] Available at:
https://hellboundbloggers.com/job-websites-for-indians/46429/
[Accessed: 25th June 2018]
Emailoverloadsolutions (2016) The six key components to properly structure business
Email messages [Online] Available at:
http://www.emailoverloadsolutions.com/blog/structure-business-email
[Accessed: 25th June 2018]
OOnline Safety and Digital Citizenship:
3 Elements of Online Safety and Digital Citizenship
· Understand what information should only be shared in specific situations (date of birth, social security, credit card, full name, etc.) and being able to identify situations where personal information should not be shared
· Knowledge of Internet best practices and common risks, including how it relates to social media, ecommerce, email, Internet searches, and viruses Articulate the meaning and real-world examples of plagiarism, digital identity theft, online bullying, cyber stalking, and hacking
JOB RELATED NEEDS FOR DEGTAL LITERACY
The Importance of Digital Skills in the Modern Workplace
In the modern workplace, digital skills are highly valued; in the future, digital skills will be vital.
The digital age is expanding into all areas of our lives, and it is not just those who work in IT that will need to be alert of this change. The House of Lords have stated that digital skills should be taught as a third core subject, and treated with same importance as numeracy and literacy.1
They went on to claim that access to the internet, in the UK, should considered as important as access to water or electricity. Added to this there is the claim that digital skills are entering all areas of work 2; medicine, entertainment, communication and retail are all turning into fields where digital skills are a must.
What Digital Skills do I Need for the Modern Workplace?
Knowing how to answer your emails, to access a company’s files on Google Drive, or to tweak or optimize a website’s code are all digital skills that are increasingly sought after in today’s job market.
Which Jobs Require Digital Skills?
The job search website Indeed has listed HTML5, MongoDB, iOS, Android and Mobile App as the fastest growing keywords found in online posts for jobs.
Coding is a job related to all of these keywords, and it is evidently an industry that is booming, but it is not the only job that requires digital skills. Marketing, customer service, retail, managing, writing and selling are all jobs associated with these keywords and all of those jobs could well require digital skills.
In short, it is safe to assume that almost all jobs will require some level digital skills. Even if they do not, it is wise for jobseekers to insure themselves against the rising need for digital skills in the workplace.
What about Automation?
Automation is the fear that, due to the digital skills gap, employers will utilise automated technology in order to fill this gap.
This fear is not unfounded7, and there are many examples throughout history where technology has replaced jobs that were once done by people. But automation should not be seen as something to be afraid of. Rather, our worry about automation should be the reasoning behind embracing digital skills in whatever way we can.
As a result, there are three things that we should be doing.
Firstly, we should be encouraging governments towards legislation that encourages the teaching of digital literacy.
Secondly, we should be supporting companies that are attempting to fill the digital teaching gap that the government has left.
Finally, as individuals we need to make sure that our digital skillset is as wide as possible for future needs.
How will Digital Skills Change the Workplace?
It is not uncommon for journalists to research, plan, write, proofread and send an article to a publisher all using their mobile phone or tablet.8
n some senses, digital skills make the workplace a freer and simpler place to navigate. A lot of work can now be done from home, or on the move, but this also brings its own set of challenges.
A consumer expects more from a company knowing that technology has made everything so much faster.
The report and survey has identified eight common requested clusters of specific Advance digital skills, all of which are crucial for job-seekers looking to advance their careers and gain entry to higher-skill and higher-paying roles:
1. Productivity software
2. Software & programming
3. Computer & networking support
4. Digital analysis
5. Digital design
6. CRM
7. Digital marketing
1. Machining & manufacturing technology
One or more specific digital skills are required in 18% of low-skill jobs, 59% for middle-skill jobs and 67% for high-skill jobs.
2. Programming, Web and App Development
At the heart of any tech product or digital service is coding. The core languages that most programming and web and app development positions need include Bootstrap, jQuery, Angular, Code Igniter, PHP/JavaScript and MySQL. These skills are listed on a regular basis in the top 10 most in-demand by employers on LinkedIn. Having a portfolio of projects demonstrating your coding skills can also help to validate your knowledge and expertise and help you land your dream role. Examples of mobile and responsive web development experience will give you an edge over other candidates.
Coding is also vital for emerging technologies such as augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR). Coding will provide AR and VR Developers with the foundation skills needed to develop the next generation of AR and VR technologies.
3. Digital Business Analysis
Digital Business Analysis helps organizations to make the right choices by providing an independent and objective mind set and applying a range of proven analysis techniques to make a convincing business case for investment in a digital solution. As digital transformation is central to all organizations in the digital economy, digital business analysis skills have become the hottest skills to have on your CV in the 21st Century. Digital Business Analysts are at the epicentre of digital transformation projects. They help organisations develop a digital ecosystem of technologies that will help drive digital transformation and business growth.
Digital Design and Data Visualization
Websites, Apps and Digital Services have one thing in common; a user interface. Any designer with experience creating effective, dynamic user experiences will be in high demand with most tech companies.
Designers can also visualize complex data to help management make vital business decisions. This skill is call data visualization. Data visualization is useful for senior leaders to gain valuable insights from data. Tools such as Tableau and Power BI are used by designers to analyse and visualize data.
4. Digital Project Management
Project management is by no means exclusively desirable to tech companies but it is a vital part of developing digital products and services in a timely and cost effective manner. An understanding of a range of methodologies such as SCRUM and AGILE will stand out on any CV. Digital Project Managers need to have a holistic understanding of how digital projects are developed - from ideation to prototype to fully developed digital product or service.
5. Digital Product Management
Another skill that is not unique to software development but one that is particularly valuable nonetheless is Digital Product Management. Software services in particular need to have a lifecycle management plan put in place. The continued growth of Software as a Service will make Product Management ever more integral to the tech sector.
6. Digital Marketing
To promote their products and services tech companies will look to digital marketing. Understanding of how to get the most value for money out of the broadest range of networks will be key here. In-demand skills for Digital Marketers include:
- Digital marketing tools
- Analytics tools
- Social media marketing
- Content marketing
- SEO
- UX (User Experience Design)
- Social Media
Some of the best PR (Public relation ) today is carried out almost exclusively through social media. Twitter, Facebook, Reddit, Instagram and countless other platforms give tech companies direct access to customers, thought leaders and evangelists. The best Tech PR managers are Social Media managers.
7. Data Science and Data Analytics
Companies gather huge amounts of data that can be immensely valuable to them if they have an Big Data Analyst who can make sense of it all. Data Scientists are in-demand by employers across the world. Glassdoor constantly feature Data Scientists in their Best Jobs Listing .Not only is Data Science an excellent career path for professionals in the digital age, but demand far outweighs supply, making Data Scientists highly employable. A recent McKinsey report showed that “The United States alone faces a shortage of 140,000 to 190,000 people with analytical expertise and 1.5 million managers with skills to make decisions based on the analysis of big data.” As data science becomes a minimum requirement for more and more manager level jobs, learning data science will help you position yourself ahead of the curve.
8. Decision Making for Leaders
Decision making is a critical for leaders in the digital age. According to the World Economic Forum, for those looking to future proof their careers, building competencies in areas that machines will be unlikely to tackle effectively (i.e. complex problem solving, creativity and problem solving) is likely the best recipe for success.
Organizations need leaders who can tap into their knowledge and experience to make rapid decisions. Behavioral economics is one route for professionals to improve their decision making abilities. Behavioral economics studies the effects of psychological, cognitive, emotional, cultural and social factors on the economic decisions of individuals and institutions. Learning this skill will improve your decision-making skills by gaining insights from the fields of cognitative and social psychology.
JOB RELATED NEEDS FOR DEGTAL LITERACY
The Learning Model: The digital literacy acquisition learning model used by these adult learners offered self-paced, tutor-facilitated instruction, built around an online learning support program.The online program, Learner Web, was designed for adult learners and offered goal-directed and learner-driven content with links to other online and offline resources and systems as well as e-portfolios. The content is customizable and shareable across different programs. Materials and reports can be accessed using different roles such as for tutors and program administrators. Some programs offered the digital literacy training as part of classes organized around other topics. Other programs used one-to-one tutoring in drop-in, open access labs. In all cases, learners were able to move at their own pace within the structure of the program. We found the flexibility of the self-paced learning model allowed learners to spend the time they had productively engaged in the content they decided was important to them. The Learner Web was also designed to accommodate the complexity of learners’ lives by keeping track of their learning for them. This allowed learners to re-enter the system at the point where they left off without needing to repeat previously learned content. They could also review what they had learned as much as they needed before deciding to move on to new content.
1. Learner Experience: How Job Seekers Move Through the Learner Path
This case study examines the digital literacy acquisition process as it was experienced by job seekers. In many respects, as these adult learners moved through their acquisition process, their experiences were similar to those acquiring digital literacy skills for purposes other than to obtain employment. For instance, analyses from the larger study of which this case study is one part, revealed a learner path common to adult learners across settings.
This learner path involves experiencing three key moments:
- (a) how digital literacy is relevant to one’s life
- (b) confronting and overcoming a fear of the technology, and
- (c) acquiring a stronger sense of self-confidence
2. The Role of the Tutor/Learner Relationship
For many job seeking learners, the support they received from tutors was integral to their success. Tutors offered support to learners in three primary ways. First, tutors acknowledged the real and urgent needs of the learners and showed awareness of the disconnect between their present situations and the long term goal of acquiring digital literacy. Second, tutors responded to the varying levels of engagement that learners exhibited often corresponding with whether they were participating in the program voluntarily or mandatorily. Finally, tutors employed unique strategies for supporting job seeking learners that were designed to offer job readiness training as part of their digital literacy acquisition process.
VERTICAL BASED REQUIREMENT
Digital literacy has transformed the traditional ways of imparting education in India and around the world. In addition to how digital literacy has impacted other areas of education sector observes
Be it in India or abroad, the first thing that digital literacy or the internet brings on the table is the ease of gathering information. Students in the western countries have been primarily relying on google searches for their school assignments, in contrast to turning the pages of outdated books that students in India do. Needless to say, gathering more information makes the work in western countries exponentially better than in India. What has lacked in India though, is not the intent to use technology but the capability to use it. Not long before, not much of India had access to high speed internet, which was overly reflected in the education system as well. Forget about learning how to ‘google’, the course books had instructions on how to turn a computer on. But gradually, internet is getting more accessible, not only at schools but also at people’s houses, as it gets cheaper. Combined with government support, cellular companies are also making internet cheaper, resulting in a positive impact in India in terms of digital-literacy. Below are some of the ways in which education in India, and in general, has been impacted the most.
Communication:
Students are now capable of communicating with each other and their teachers in real time. Earlier, it was a hassle for students to collaborate on a project. Especially during vacations, it was impossible for them to check what the other guy is doing or to get feedback from teachers. Now students have a number of ways to communicate, like phone calls, internet messengers, skype etc. They can even manage work better as teachers encourage them to use work management software like Trello and Asana.
Information gathering:
Not only is the world changing, but it is changing at a faster pace every day. Therefore, it is impossible to print the most updated information in school books every year, and update them frequently. What can be changed frequently though, is a web page. Internet has seen an increasing number of students from India, looking up information related to their school assignments. Just last year, the year-on-year growth of internet users in India was 23%, a huge number, compared to the world average of 10%.
Online learning:
With the world moving towards skill based job opportunities, people are realising that having in-demand skills is more important today than having a degree. Therefore, they turn to internet for micro-courses like ‘Digital Marketing’, ‘Web Development’, etc. The number of people paying to learn online, in India, rose from fairly none at the start of this decade to 1.6 million in 2016, resulting from two years of 100% growth, as per a research conducted by KPMG. Additionally, there are plenty of other websites which provide free online courses and tutorials. An example of this can be seen on Hackr.io which hosts links of several hundreds of websites, which offer web development tutorials available on the internet, most of which are free.
Career planning:
With technology and automation in picture, a lot of jobs are getting obsolete but many new ones are coming up. The challenge, however, is to make students aware of them. Traditionally, it is parents who decide for their children, but we all know how ineffective that is. These days, internet is enabling students to break through the tradition. Students are now constantly updated about what’s trending in market, through networking sites like Linkedin and Facebook. Moreover, start-ups like iDreamCareer have come up with online tests and counselling services, to further help the students in making their career decisions.
Modernising schools:
The most drastic change that digital brought about in education is the technology we use at school. The most revolutionary one has been digital boards in classrooms. This has led to students associating words with graphics from a very early age, and is thereby improving their learning skills. Students develop a skill of learning through videos lessons, a skill which later manifest into them using YouTube and Khan Academy for educational content.
Gamification of education:
Not everyone learns alike, some prefer to learn by reading in black and white, while some like to be taught through games. Digitalisation of education brought a huge array of online games which help let children learn easily. This also lets teachers get a thorough understanding of what a student’s learning behaviour is like.
Showcasing talent:
With internet and all the platforms it has to offer, it is easier for students to showcase their talent and work. Students often make use of platform like SlideShare and YouTube to publish their school assignments. A lot of design students post their art on Dribbble and Behance, and go head on against the professionals. This opens them up to feedback from billions of people from the internet community and an equal chance to prove their metal.
Digital literacy is a hot topic these days, and we’ve previously written about the importance of it for today’s students and what teachers need to know about helping them use technology effectively to enhance modern communication.
But although the need for digital literacy is clear, actually teaching and using technology in educational settings can still be a bit of a puzzle. Of course, most students are already comfortable using a wide range of digital tools, but this doesn’t necessarily mean they know how to use these same tools for learning purposes.
Inclusion facilitator Dr. Kristin Bertolero from the New Jersey Coalition for Inclusive Education (NJCIE) frequently works with educators who need guidance on how to instruct students in various forms of digital literacy. She notes that because technology is not intuitive and must be learned and practiced, there’s a lot of trial and error on the way to mastery.
“It’s easier [for teachers] to use pre-made pencil and paper resources that they know will meet the requirements of the assignment and earn a good grade,” says Bertolero.
“But exposure to technology, opportunities for problem solving, and trial and error are what make someone an expert in technology. If we can get students developing these skills at a young age, they’ll continue to learn as the field progresses and their career opportunities will increase astronomically.”
She points out that technology shouldn’t be viewed as a substitute for traditional learning activities, because although this might keep students engaged, it doesn’t help them develop 21st century problem solving skills. Instead, students should be given opportunities to use technology to solve problems and be creative. Then, because of their love of learning and being challenged, using technology in their field will become an obvious continuation of their passion.
“Even if your students don’t go into the technology industries, being able to use it and continue their own self-directed learning can benefit them in ways we cannot presently foresee,” she says.
Unfortunately, because digital literacy is still one of those buzzwords that tend to get thrown around without specifics, it can be difficult to envision what it actually means to be digitally literate.
With this in mind, we’ve rounded up some examples of what digital literacy in education looks like.
1. Emphasize the importance of critical thinking
- The majority of media we consume today comes from online sources, some of which are more credible than others. Of course, the fact that so much information is readily available to anyone with an internet connection is a decidedly positive thing. But it also means that today’s students are more susceptible to subliminal messages, misinformation, and fake news.
- With this in mind, a huge part of teaching digital literacy is helping students become critical consumers of information. Start by encouraging students to ask questions and then find answers by going straight to the source and checking for objectivity.
2. Use social media for learning and collaborating
- Today’s students are already active on social media, and in many cases they may already be more adept at using it than their teachers. So the focus shouldn’t be on introducing students to the ins and outs of social media, but on demonstrating how it can be used in an educational context.
- For example, Pinterest boards can be used for providing and receiving feedback during group projects, Twitter can be used create polls for research purposes or find expert sources, and Facebook or LinkedIn groups can be used to connect and collaborate with their peers.
3. Provide guidance on how to avoid plagiarism
- Although the Internet hasn’t necessarily made plagiarism easier, it has changed the way it happens, and students may now be at risk of plagiarising even without meaning to. A study published in the journal Higher Education, found that many students don’t understand plagiarism, but they do want more information on what it is and how to avoid it.
- For example, students often ‘borrow’ ideas or use phrases they find online without properly citing the original work, and are later surprised to learn that this constitutes plagiarism. So another important aspect of becoming digitally literate is learning how to avoid plagiarism by taking good notes, using citations and quotes, and properly supporting a discussion with references.
4. Teach students to manage their online identity
- Regardless of whether we consciously manage it or not, we all leave a digital footprint and have an online identity. Students who have grown up using social media are more likely to take it for granted that their data is stored online, and as a result, may not give as much thought to safeguarding their privacy by managing their privacy settings, reading privacy policies, and being as respectful in their online interactions as they would be in person.
- But in the same way that not managing an online identity can have negative implications, taking steps to build a positive one can be hugely beneficial to students’ career prospects. With this in mind, learning how to safeguard privacy online but also how to share the right information and content are important aspects of a well-rounded digital literacy education.
5. Help students manage digital distractions
- Digital tools and online resources have made learning more effective in many ways, but they’ve also brought new distractions with them. Research shows that many of us struggle with digital distraction, which can make us feel distant and drained, and even reduce our enjoyment of experiences. Juggling multiple media streams can also lead students to multi-task, which isn’t a good thing considering that research shows that students who multi-task tend to have lower grades.
- So the ability to manage distractions while utilising digital tools for learning and professional purposes is another digital literacy skill that shouldn’t be overlooked. Some examples of distraction-management strategies include taking tech breaks throughout the day, muting notifications while studying, using productivity tools, and setting goals around technology use.
6. Provide authentic contexts for practice
- Another important part of teaching digital literacy is finding ways for students to practice using technology in ways that mirror its real world uses, whether this means giving students opportunities to practice building their own websites and apps, or respectfully engage in online discussions.
- For example, when teaching students about the important of managing their online identity, you could have them research themselves online to find out what a potential employer would see. You could follow this up with a discussion about their findings, and have them list some of the things they were proud of as well as some of the things they’d like to change.
7. Guide students out of their comfort zone
- We all have a comfort zone when it comes to technology, but if we want students to become innovative and well-rounded users of technology, it’s important to guide them out of their comfort zone whenever possible. Of course, this will mean something different for each student.
- For example, some students may already be adept at communicating in short and distinct paragraphs and hashtags on Twitter or Instagram, so moving out of their comfort zone might mean sharing their opinion through a more in-depth blog post. In other cases, students might already have experience with blogging, in which case they might be interested in trying something a bit more out-of-the-box such as video journals or podcasts.
- Whatever the case may be, giving students more freedom of choice and encouraging them to use technology in new and creative ways is one of the best ways to help them hit the ground running once they enter the workforce.
1. Introduction
- What is important for educators and managers to consider when teaching programming, digital design and digital literacy in secondary education? Are there didactic methods specifically related to digital design and digital production? This article presents a model for planning and evaluating teaching in programming, digital design and digital literacy.
- The model was developed for secondary education in Denmark in collaboration with teachers. The teachers were part of the ROBO learning project (2018-2020)1 which included four upper secondary schools, with most students ranging from 16 – 19 years of age, and five primary and lower secondary schools, focusing on students ranging from 13 – 15 years of age. The upper secondary schools encompassed general Upper Secondary School,Technical and Commercial Upper Secondary School and Vocational Education and Training2. In addition, the model was used to evaluate 18 of 35 courses in digital production and digital literacy in the “crossingIT” project(2017-2019).3
- The learning perspective in this article is based on experiential, collaborative and participatory learning processes as described by Kolb (1984), Wenger (1998), Papert (1993), Schön (2001), Rusk et al (2008), Resnicket al (2009) and Majgaard (2015), among others. Learning often takes place when the students actively participate and experience new subject matter. These experiences need to be explicitly reflected upon in the community of practice in the classroom.
2. Didactic model for the development and evaluation of courses
- This section presents a model for evaluation of teaching and lesson planning in programming, digital design and digital literacy. The model can be used for exploring all the relevant aspects in the design phases of a course and its further development. Furthermore, the model can assist in systematically evaluating existing courses.
- The model was developed in collaboration with a selected group of teachers in the ROBOlearning project. In three workshops and several project seminars, the teachers explained their approach to planning and conducting teaching in digital literacy and production. They explained their ideas in keywords and provided elaborate examples of planned and conducted teaching in the field. In the ROBOlearning project, the teachers are now documenting their teaching using the four elements in the model. As a supplement, we developed questions to support and operationalise the model. Supportive questions as well as courses can be found on the project’s website.
- In the development phase, a round as well as a linear phase model illustrating the four elements was presented to the teachers. They preferred the round model. Learning and teaching is often circular, iterative and complex. The round model underlines that the starting point could be anywhere. Additionally, the model balances a technology and learning goal-driven approach by presenting complementary approaches to didactic planning.
3. Teaching design
Teaching design includes common elements of lesson planning such as learning objectives, activities, scaffolding and practical organisation: see figure 1. In addition, the teacher must decide on the learning output the students must produce and how it should be evaluated (Gynther, 2010; Hiim and Hippe 2007). Traditionally, learning output includes written texts (such as reports) and oral presentations. When the subject area extends to IT and technology, the products become more multi-faceted and often digitally interactive. They may include homemade computer games, digital simulations, apps, programs, code examples, student-produced video tutorials, robotic artefacts, video material explaining the students’ digital products, etc. The teacher should formulate specific requirements for these digital products (for example in games: the number of levels, start and end scenes). In addition, the requirements can relate to a thematic framework such as, for example, climate or future scenarios.
4. Digital production
The dimension of digital production consists of methods for digital production, e.g. well-ordered problems, wellprepared running codes constructed by the teacher (“worked example” Caspersen et al), video teasers, all of which form the basis for the students' products. It is important that the students not only copy the “worked examples”, but that the running examples should kick-start their own further digital production. The examplesensure that all students get a head start, avoiding some of the frustrations and avoiding “getting stuck” from the start. There is, however, also a risk that over-developed examples block creativity (Majgaard, 2017). In other words, the worked examples should create a low floor and a high ceiling (Brennan and Resnick, 2012).
Explore this Link
Common Core requires students be able to translate quantitative data into visual forms. Infographics help students create shareable visualizations that tell a story or communicate an idea. Learn how to make an infographic with easel.ly .
For young children, emojis can be used to encourage them to share how they are feeling. The oldest form of literacy, these symbols provide access to a living language that enables them to express themselves in ways that words cannot always do.
Press window key + dot ( .) togethe to insert emojis anywhere try now!!!..✨✨✨✨✨
#3. Google Docs teaches data collaboration.
All students can share class data through Excel documents on Google Docs. An easy and free collaborative feature alerts you when others are online and editing information. Liberally use Google docs as it is an important professional skill, as many college classrooms and work environments are utilizing this tool too.
- docs.new (Google Docs)
- sheets.new (Google Sheets)
- slides.new (Google Slides)
- keep.new (Google Keep)
- forms.new (Google Forms)
- cal.new (Google Calendar)
- meeting.new (Google Calendar)
- sites.new (Google Sites)
#5. Installing modern web browsers
For now, we'll install a couple of desktop web browsers to test our code in. Choose your operating system below and click the relevant links to download installers for your favorite browsers:
- Linux: Firefox, Chrome, Opera, Brave.
- Windows: Firefox, Chrome, Opera, Microsoft Edge, Brave (Windows 10 comes with Edge by default; otherwise, you should install an alternative browser).
- macOS: Firefox, Chrome, Opera, Safari, Brave (macOS and iOS come with Safari by default).
Before going on, you should install at least two of these browsers and have them ready for testing.
Under the Indian GST, goods and services are categorized into different tax slabs, including 5%, 12%, 18%, and 28%. Some essential commodities are exempted from GST, Gold and job work for diamond attract low rate of taxation.
GST registeration video link : https://www.gst.gov.in/help/video/tdsparta
GSP [Goods and service providers]:
Part – 1: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLwd4X2n8jgXw2EstgE4N6zCnHUCIYuHp3
Part-2: https://www.gst.gov.in/help/video/tdspartb
https://www.gst.gov.in/help/enrollmentwithgst
GST Registration:
https://tutorial.gst.gov.in/cbt/registration/composition/course/story_html5.html
Check your Fitness Level Score, Track your Steps.Track your Sleep, Track your calorie intake,Be Part of Fit India Events, Get customized DietPlans Age-wise fitness level
Fitness Mantra
Fit India Mission encourages people to become part of Fit India Movement by inculcating at least 30-60 minutes of physical activities in their day to day lives. The mission of the Movement is to bring about behavioral changes and move towards a more physically active lifestyle.
Link to register as a seller at flipkart
https://seller.flipkart.com/sell-online/sell-watch-online
https://seller.flipkart.com/index.html#signUp/accountCreation/new
Becoming a Flipkart seller is that easy 🎉
How to sell on Flipkart: https://youtu.be/NzP3vmABTD0
E-commerce training:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GjdGqf_3oSs
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qLPT7bzlXc4&list=PLvGVY4CVYs_aD6aD__62ipoGYRALrJZB5
Payment is done by NEFT and the seller account will be live within 5-7 working days of registration process.
E-Learning
https://youtu.be/39E5bNSlaIU?list=PLvGVY4CVYs_aD6aD__62ipoGYRALrJZB5
Select the state by
clicking on the map to visit State Government website.
India at a
Glance| National Portal of India
National Portal
of India provides a single-window access to
information and services that are electronically delivered from all Government
Departments, Institutions and Organizations.
India at a
Glance| National Portal of India
<iframe width="949" height="534"
src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/39E5bNSlaIU?
https://youtu.be/39E5bNSlaIU?list=PLvGVY4CVYs_aD6aD__62ipoGYRALrJZB5&t=227
Courses
Offered – ICAR-Indian Agricultural Statistics Research Institute, Government of
India
Resources for ebooks, MCQ with Answers
Registration at Sehaj : (2890) Sahaj Mitr
Registration Video || Sahaj Mitr Kaise Bane || Sahaj Registration Process -
YouTube
Google sheet multiuser entry form : (2890) Google Sheet - Multi
User Data Entry Form - YouTube
What is fishing
It is used to harm you, URL must start with https and check lock icon also
Knowing how to answer your emails, to access a company’s files on Google Drive, or to tweak or optimize a website’s code are all digital skills that are increasingly sought after in today’s job market.
#2 Get facts & Insights on topics that really matters to you at or https://www.statista.com/
#3. Best Indian blogs to Read from popular Indian bloggers or https://bloggerspassion.com/best-indian-blogs-to-read/
#4. Optimize your image using this tool : https://icompress.indroid.in/icompress.indroid.in [https://icompress.indroid.in/]
#5. Explore free images at [https://www.freeimages.com/] and at [ https://www.freepik.com/]
#6. Keyword research tool : [https://keywordplanner.net/] or at [https://www.jaaxy.com/ ]
#7. Blog Topic IDEA Generator at https://www.hubspot.com/blog-topic-generator or at [https://www.portent.com/tools/title-maker/] or at [http://www.buildyourownblog.net/the-blog-post-ideas-generator/] OR at [ https://www.inboundnow.com/apps/kill-writers-block/] or at [https://buzzsumo.com/]
#8. Check the website speed using tools : Sitechecker [ https://sitechecker.pro/] or
[https://gtmetrix.com/ ] or [ https://www.uptrends.com/tools/website-speed-test ] or
[https://smallseotools.com/page-speed-test/] or [ https://tools.pingdom.com/ ]
#9. Website Audit tool Screaming Frog : Download Screaming frog
[ https://www.screamingfrog.co.uk/seo-spider/]
#10. Learn Keyword research process : at [ https://mangools.com/blog/keyword-research/]
#11. Create sitemap of your blog at [ https://www.xml-sitemaps.com/ ]
#12. Download E-books : [ https://try.alexa.com/resources/ ]
#13. Most valuable resource about SEO in Internet - lots of charts and simple tutorials to follow
https://d2v4zi8pl64nxt.cloudfront.net/seo-cheat-sheet.pdf - SEO cheat sheet - really worth to print! :-)
#14. Explore state chart reports to explore growth opportunities by Google at [https://economicimpact.google.com/]
#15. This Link provides free SSL certificate for everyone. Any self-respecting hosting will provide you with a basic SSL certificate for free at present. [ https://letsencrypt.org/]
Having SSL certification is considered as one of the SEO ranking factor in the eyes of Google.
========================================================================
- Sending Emails
- Using chatgpt
- Chatting
- Using social media
- Searching anything on google
- Creating and editing video
- Creting a list of items on ms-word
- Applying functions & formulas in Excel
- Creating eye catchy presentations
- Applying transformation on image
- Creating and sharing hyperlinks
- Your presence on social media platforms reflects your digital literacy too
- Create your own social media channel
- Create your own blog or website
- Create your own webpage using HTML
- Effectively use Google docs,slides and sheets
- Hindi translation
- Scanning
- Voice search
- App downloading
- Software or operating system downloading and installation
- Internet connectivity
- Hardware connectivity
- Online payment tools usage like debit card credit card paytm
- Online conferencing plateform usage capability like screen sharing meeting link creation , inviting other users and all
- Bitly : URL shortning
- Uploading files and folder and even image on Google drive and creating a sharable link also with the community
- Usage of wetransfer link sharing
- Usage of canva for creating social media post or ppt or banners or image or post etc.
- Normal phone calls, video call, adding people to running calls, call recording , listening a call in fast medium or slow track.
- Plagiarism checker
- Keyword research
- Email tester
- Writing an effective mail
- Article rewriter
- Grammmerly checking
- Adding extension to crome or other browser
- Change your search enging
- Create logo using canva
- Explore application areas of “Digital Literacy” and how Digital literacy will be applied in these areas.
- Web browser?
- Search engines
- Wiki, blogs
- Photoshop, coral draw
- Google ads creation
- Website and hosting
- Content creation strategy using spoke and hub technology
- 6-Hat rule
- Inforgraphics creation
- E-governance
- https://indiaai.gov.in/ The National AI Portal of India is now called INDIAai Portal. Stay informed with the latest AI articles, news, and videos. Engage in a diverse community, ...
- Passport create online
- Visa create
- Name of online learning platform like course era ,simpliearn, futureskills etc.
- Google certification
- How to use multi-medial
- Investigate a specific topic
- Typing master or monkey type
- Using online media without any knowledge or guidelines on how to judge wheather the information is correct or not.
- Google map usage
- Online movie ticket booking
- Cab booking using uber or ola
- Order your food online
- Travel bookings
- Policy purchase and compare
- Buy car
- Want to take admission in any university
- Going for an interview for the job
- Search your job using naukri or indeed or
- Create PDF
- Covert one file type to another
Basic operation of Computer includes
Create and manage files and folders tree, use accessories utilities of windows OS
2.
Entering and editing text in
document.
3.
Apply formatting features on
text like B, I, U, Font type, colour and size. Apply features like bullet,
Numbering.
4.
Create document insert images,
format tables.
5.
Create and manipulate tables
6.
Entering and editing Data in
worksheet
7.
Apply formulas and functions in
the sheet
8.
Use graphics and auto shapes in
excel sheet
9.
Create and manipulate excel
charts
10.
Create pay bills, pay slips,
electricity bills using excel
11.
Print sheet using print area
12.
Basic operations of power
point, Create ppt and insert and delete slides
13.
Create project presentations,
lectures presentations
14.
Apply basic formatting features
in presentations
15.
Working with drawing tools,
video, audio, link to video etc.
Think critically about body image
Think critically about body
image
Teachers can use
digital photography and Snapchat filters to encourage children to think
critically about the images they are seeing. Pupils could also be invited to
speak positively about themselves and others. ClassFlow Marketplace holds
a range of different body image resources available to teachers.
Encourage pupils to think
ethically
Teaching digital
literacy requires an ethical dimension. Students need to understand what it
means to behave well online and how to act in environments where the public and
private worlds are blurred. One way teachers can approach this is by
challenging their students to think about what information is readily available
about them online, and how others including any future employers might view and
react to this.
Digital
literacy (Practical 8 hrs)
1. Computer Fundamentals : 3 Elements of Computer
Fundamentals
· Find and open files, save in
different locations
· Understanding of software
programs: copy and paste functionality, formatting(fonts, font size, color, text
alignment), etc.
· Basic knowledge of computer
components: monitor, processor, motherboard,power supply, RAM, hard drive, and
inputs
2. Coding: 3 Elements of Coding
· Understanding of the key
structures used in programming and coding languages
· Develop fluency in the syntax of programming
or coding language
· Use coding and programming
languages to solve problems and create products
3.
Keyboarding : 3 Elements of Keyboarding
· Effective QWERTY keyboard use
without assistance
· Daily typing practice to improve
technique, accuracy, and speed
· Knowledge of basic keyboarding
shortcuts and commands
4. Online Safety and Digital Citizenship: 3 Elements of Online Safety and Digital
Citizenship
· Understand what information
should only be shared in specific situations (dateof birth, social security,
credit card, full name, etc.) and being able to identifysituations where
personal information should not be shared
· Knowledge of Internet best
practices and common risks, including how it relatesto social media, ecommerce,
email, Internet searches, and virusesArticulate the meaning and real-world
examples of plagiarism, digital identity theft, online bullying, cyber
stalking, and hacking
5. Computational Thinking : 3 Elements of Computational Thinking
· Transferable problem-solving
process that leverages the power of computing tofind solutions
· Develops the dispositions and
attitudes to have confidence, persistence andtolerance for ambiguity while
collaborating to achieve a common goal
· Uses patterns, modeling,
abstraction, and decomposition in algorithmic design, implementation, and
testing to develop efficient and effective solutions
JOB RELATED
NEEDS FOR DEGTAL LITERACY
The Importance of Digital Skills in the Modern
Workplace
In the
modern workplace, digital skills are highly valued; in the future, digital
skills will be vital.
The
digital age is expanding into all areas of our lives, and it is not just those
who work in IT that will need to be alert of this change. The House of Lords
have stated that digital skills should be taught as a third core subject, and
treated with same importance as numeracy and literacy.1
They
went on to claim that access to the internet, in the UK, should considered as
important as access to water or electricity. Added to this there is the claim
that digital skills are entering all areas of work 2; medicine,
entertainment, communication and retail are all turning into fields where
digital skills are a must.
What Digital Skills do I Need for the Modern
Workplace?
Knowing
how to answer your emails, to access a company’s files on Google Drive, or to
tweak or optimize a website’s code are all digital skills that are increasingly sought
after in today’s job market.
Which Jobs Require Digital Skills?
The job
search website Indeed has listed HTML5, MongoDB,
iOS, Android and Mobile App as the fastest growing keywords found in online
posts for jobs.
Coding
is a job related to all of these keywords, and it is evidently an industry that
is booming, but it is not the only job that requires digital skills. Marketing,
customer service, retail, managing, writing and selling are all jobs associated
with these keywords and all of those jobs could well require digital skills.
In short,
it is safe to assume that almost all jobs will require some level digital
skills. Even if they do not, it is wise for jobseekers to insure themselves
against the rising need for digital skills in the workplace.
What about Automation?
Automation
is the fear that, due to the digital skills gap, employers will utilise
automated technology in order to fill this gap.
This
fear is not unfounded7, and there are many examples throughout history where
technology has replaced jobs that were once done by people. But automation
should not be seen as something to be afraid of. Rather, our worry about
automation should be the reasoning behind embracing digital skills in whatever
way we can.
As a
result, there are three things that we should be doing.
Firstly,
we should be encouraging governments towards legislation that encourages the
teaching of digital literacy.
Secondly,
we should be supporting companies that are attempting to fill the digital
teaching gap that the government has left.
Finally,
as individuals we need to make sure that our digital skillset is as wide as
possible for future needs.
How will Digital Skills Change the Workplace?
It is
not uncommon for journalists to research, plan, write, proofread and send an
article to a publisher all using their mobile phone or tablet.8
n some
senses, digital skills make the workplace a freer and simpler place to
navigate. A lot of work can now be done from home, or on the move, but this
also brings its own set of challenges.
A
consumer expects more from a company knowing that technology has made
everything so much faster.
Service Assistant, Environmental Services
Bobbie
Wells’ workdays start at 7 a.m., when she begins cleaning patient rooms
according to a detailed plan designed to stop the spread of infection.
Her entry-level
job requires only basic digital-literacy skills, centered on using mobile apps
for communications and task management.
Production Supervisor, Food and Nutrition
Services
What’s the most efficient way to make
hundreds of gallons of gravy a week?
In the lower levels of Christiana Hospital,
Dante Pozzi initiates the process via technology, using a digital touch screen
to program a massive kettle.
“Food service is no different than any
other industry,” he said. “Tech is changing everything.”
Registered Nurse
In Brianna Buzzuro’s four years as a
nurse, her job has changed dramatically.
“All of our documentation used to be on
paper,” Buzzuro said. “Now, every moment I’m not with a patient, I’m on the
computer.”
Corporate Director, Health Information Management
Services
Stefanie Brumberg views herself as a
“hub,” connecting Christiana Care’s direct-care providers and information
technology staff.
“I’m on conference calls most of the
day, usually about the best way to capture the information we need to capture,”
she said. “There’s just so much content to synthesize.”
The report identified eight common
requested clusters of specific digital skills, all of which are crucial for
job-seekers looking to advance their careers and gain entry to higher-skill and
higher-paying roles:
1. Productivity software
2. Software & programming
3. Computer & networking support
4. Digital analysis
5. Digital design
6. CRM
7. Digital marketing
1. Machining &
manufacturing technology
One or
more specific digital skills are required in 18% of low-skill jobs, 59% for
middle-skill jobs and 67% for high-skill jobs.

2. Programming,
Web and App Development
At the heart of any tech product or digital
service is coding. The core languages that most programming and web and app development positions
need include Bootstrap, jQuery, Angular, Code Igniter, PHP/JavaScript and
MySQL. These skills are listed on a regular basis in the top 10 most in-demand
by employers on LinkedIn. Having a portfolio of projects demonstrating
your coding skills can also help to validate your knowledge and expertise and
help you land your dream role. Examples of mobile and responsive web
development experience will give you an edge over other candidates.
Coding is also vital for emerging
technologies such as augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR).
Coding will provide AR and VR Developers with the foundation skills needed to
develop the next generation of AR and VR technologies.
3.
Digital Business Analysis
Digital Business Analysis helps organizations to make the
right choices by providing an independent and objective mind set and applying a
range of proven analysis techniques to make a convincing business
case for investment in a digital solution. As digital transformation
is central to all organizations in the digital economy, digital business
analysis skills have become the hottest skills to have on your CV in the 21st
Century. Digital Business Analysts are at the epicentre of digital
transformation projects. They help organisations develop a digital ecosystem of
technologies that will help drive digital transformation and business
growth.
Digital Design and Data Visualization
Websites, Apps and Digital Services have
one thing in common; a user interface. Any designer with experience creating
effective, dynamic user experiences will be in high demand with most tech
companies.
Designers can also visualize complex data
to help management make vital business decisions. This skill is call data
visualization. Data visualization is useful for senior leaders to gain valuable
insights from data. Tools such as Tableau and Power BI are
used by designers to analyse and visualize data.
4. Digital
Project Management
Project management is by no means
exclusively desirable to tech companies but it is a vital part of developing
digital products and services in a timely and cost effective manner. An
understanding of a range of methodologies such as SCRUM
and AGILE will stand out on any CV. Digital Project Managers need to
have a holistic understanding of how digital projects are developed - from
ideation to prototype to fully developed digital product or service.
5. Digital
Product Management
Another skill that is not unique to
software development but one that is particularly valuable nonetheless is Digital Product
Management. Software services in particular need to have a lifecycle
management plan put in place. The continued growth of Software as a Service
will make Product Management ever more integral to the tech sector.
6. Digital
Marketing
To promote their products and services tech
companies will look to digital marketing. Understanding of how to get the
most value for money out of the broadest range of networks will be key here.
In-demand skills for Digital Marketers include:
Digital marketing tools
Analytics tools
Social media marketing
Content marketing
SEO
UX (User Experience Design)
Social Media
Some of the best PR today is carried out
almost exclusively through social media. Twitter, Facebook, Reddit, Instagram
and countless other platforms give tech companies direct access to customers,
thought leaders and evangelists. The best Tech PR managers are Social Media
managers.
7. Data
Science and Data Analytics
Companies gather huge amounts of data that
can be immensely valuable to them if they have an Big Data Analyst who can make
sense of it all. Data Scientists are in-demand by employers across the world.
Glassdoor constantly feature Data Scientists in their Best Jobs Listing .Not only is Data Science an excellent
career path for professionals in the digital age, but demand far outweighs
supply, making Data Scientists highly employable. A recent McKinsey report
showed that “The United States alone faces a shortage of 140,000 to 190,000
people with analytical expertise and 1.5 million managers with skills to make
decisions based on the analysis of big data.” As data science becomes a minimum
requirement for more and more manager level jobs, learning data science will
help you position yourself ahead of the curve.
8. Decision
Making for Leaders
Decision making is a critical for leaders
in the digital age. According to the World Economic Forum, for those looking
to future proof their careers, building competencies in areas that machines
will be unlikely to tackle effectively (i.e. complex problem solving,
creativity and problem solving) is likely the best recipe for success.
Organizations need leaders who can tap into
their knowledge and experience to make rapid decisions. Behavioral
economics is one route for professionals to improve their decision making
abilities. Behavioral economics studies the effects of psychological,
cognitive, emotional, cultural and social factors on the economic decisions of
individuals and institutions. Learning this skill will improve your decision-making
skills by gaining insights from the fields of cognitative and social
psychology.
JOB RELATED
NEEDS FOR DEGTAL LITERACY
The
Learning Model: The digital literacy acquisition learning model used by these adult
learners offered self-paced, tutor-facilitated instruction, built around an
online learning support program.The online program, Learner Web, was designed
for adult learners and offered goal-directed and learner-driven content with
links to other online and offline resources and systems as well as
e-portfolios. The content is customizable and shareable across different
programs. Materials and reports can be accessed using different roles such as
for tutors and program administrators. Some programs offered the digital
literacy training as part of classes organized around other topics. Other
programs used one-to-one tutoring in drop-in, open access labs. In all cases,
learners were able to move at their own pace within the structure of the
program. We found the flexibility of the self-paced learning model allowed
learners to spend the time they had productively engaged in the content they
decided was important to them. The Learner Web was also designed to accommodate
the complexity of learners’ lives by keeping track of their learning for them.
This allowed learners to re-enter the system at the point where they left off
without needing to repeat previously learned content. They could also review
what they had learned as much as they needed before deciding to move on to new
content.
1.
Learner Experience: How Job Seekers Move Through
the Learner Path
This
case study examines the digital literacy acquisition process as it was
experienced by job seekers. In many respects, as these adult learners moved
through their acquisition process, their experiences were similar to those
acquiring digital literacy skills for purposes other than to obtain employment.
For instance, analyses from the larger study of which this case study is one
part, revealed a learner path common to adult learners across settings.
This learner path involves
experiencing three key moments:
(a) how digital
literacy is relevant to one’s life
(b) confronting
and overcoming a fear of the technology, and
(c) acquiring a
stronger sense of self-confidence
2. The Role of the Tutor/Learner Relationship
For many job seeking
learners, the support they received from tutors was integral to their success.
Tutors offered support to learners in three primary ways. First, tutors
acknowledged the real and urgent needs of the learners and showed awareness of
the disconnect between their present situations and the long term goal of
acquiring digital literacy. Second, tutors responded to the varying levels of
engagement that learners exhibited often corresponding with whether they were
participating in the program voluntarily or mandatorily. Finally, tutors
employed unique strategies for supporting job seeking learners that were
designed to offer job readiness training as part of their digital literacy
acquisition process.
3. Digital Literacy
Acquisition Case Studies
Corrections and Re-entry
Volunteers in an Adult Literacy Library Program
Job Seeking Learners
4. Digital Literacy
Acquisition Policy Brief
Community Connections
5.
The
Learner Web offered learners the option of content in English or Spanish. Labs
often had bilingual (English/Spanish) tutors available. In terms of the tutors’
capability to meet individual learner needs as they arose, tutors were able to
check-in, guide, and encourage learners as they worked. They were available to
answer learner questions in an individualized and flexible way, providing
examples as needed. In this model learners got support when they needed it and
would work independently otherwise. Within the online platform, digital
literacy content is organized into modules called learning plans. Learning
plans are grouped into three main content areas. These are (a) Computer and
Internet skills, which teaches basics such as mousing and keyboarding, as well
as finding information online, using email, Internet security and safety, and
using popular social network platforms; (b) Broadband Consumer Education, which
helps learners become savvy consumers of computer hardware and broadband subscription
services; and (c) Introduction to Career Paths, which orients learners to basic
career path concepts and connects them with local career path programs. These
learning materials were included in part to help learners see what new job
possibilities might exist for them once gaining computer and digital literacy
skills.
SOCIAL SHARING
The Potential for
Social Media in Your Science Classroom
How
can social media be effectively integrated into a science classroom? With your
school district or administration’s approval, here are eight tips to get your
class social media savvy this school year. When possible, make sure to set all
accounts to private settings to ensure students are safely sharing their
information and their learning experience.
1. Twitter
generates science news in the classroom.
Ask
students to follow scientists ,
journalists, and Twitter chats that support the content you are currently
teaching. Help students develop radars for quality scientific sources on
Twitter, the ability to recognize opinion, and the need for the unabridged
version of a tweet. Need help on how to integrate Twitter into your classroom?
KQED has a “ Guide to Using Twitter in Your Teaching Practice ” as
part of their Do NOW series that aims to get students safely engaged in current
issues through social media.
2. Feedly is a news aggregator that is perfect for
classrooms and research projects.
There
is more information available today to students than in any point in history.
Students can learn to filter and curate content based on their interests or
research on Feedly .
Create a class account to save and share daily science news stories with
students. What is on NOVA Education’s Feedly? Scientific American , NPR’s Science Desk , Smithsonian Magazine and
of course, NOVA Next !
3. Twitter reveals
STEM diversity to students.
The
beauty of Twitter is that students have front row access to academics and
professionals in their fields of interest. Here at NOVA Education, we all love
following Neil deGrasse Tyson , but
there are even more scientists on Twitter who challenge the stereotype of what
a scientist should look or act like. Here and here are
two lists to get you started.
4. Vine allows
students to document and share science happening in the classroom and their
community.
Below
is a video from KQED Education that explains how to use the app Vine , which creates looping six to
seven-second videos that can be shared. Meteor shower tonight? Observing
environmental pollution in your neighborhood? Cool physics experiment in class?
Document and share video to support student engagement in science.
Make short social video loops With Vine
5. Easel.ly helps
meet Common Core standards with infographics.
Common
Core requires students be able to translate quantitative data into visual
forms. Infographics help students create shareable visualizations that tell a
story or communicate an idea. Below is another video from KQED Education that
explains how to make an infographic with easel.ly .
6. Google Docs
teaches data collaboration.
Encourage
students to share class data through Excel documents on Google Docs. An easy
and free collaborative feature alerts you when others are online and editing
information. Teaching students how to use Google docs is an important
professional skill, as many college classrooms and work environments are
utilizing this tool too.
7. Pinterest allows students to curate visuals
related to science.
Set
up a classroom Pinterest account for students to share images they find for
research projects or writing prompts. The NOVA Education team loves the Women in STEM and Science and Nature boards!
8. WordPress
blogging can aid in peer-to-peer learning.
Set
up a WordPress class
account for the year and pose daily questions or writing prompts based on
readings. NGSS encourages more writing in science classrooms and collaborative,
peer-to-peer feedback is the main ingredient in college writing courses. Why
not start now?
John
Fallon believes the concerns around social media in the classroom are
legitimate and “that social norm is going to be in flux for the foreseeable
future.” But as an educator he has found safe alternatives around these
challenges, like using email addresses within the school system or closing
video sharing to only his students. Fallon and Paul Darvasi’s experiences echo
that there is no one size fits all digital literacy plan. Start small with one
lesson plan and expand from there. Experimentation is key.
In
your class, come up with a list of ways we communicate online. Here are a few
examples:
· Social networking sites (Facebook,
Twitter, and Instagram)
· Instant Messaging
Services (Messenger/Whatsapp/Viber/Snapchat)
· Video/Audio Conferencing
Services (Skype/FaceTime)
· Live streaming (Facebook, YouTube,
Netflix)
· Blogs
· Vlogs (YouTube)
· Email (Gmail, Outlook, Yahoo,
Live)
· Chatrooms
· Online Gaming (text and audio
communication)
· Forums
· Dating Sites (Tinder, PoF)
What We
Share Online:
·
Email (Gmail,
Outlook, Yahoo, Live)
·
Chatrooms
·
Online
Gaming (text and audio communication)
·
Forums
·
Dating
Sites (Tinder, PoF)
What We
Share Online:
Young people are spending
more time online and can often not realise how much information they are
actually sharing with the world.
Help your students
practice safe online communication by making them aware of our top tips to
consider when sharing online.
1. Share only what
you are comfortable with. Make sure you have permission to post
pictures of other people and that they have yours before posting.
2. It may sound obvious
but some people may not realise the risks of sharing their location online.
Lots of apps now allow us to share exactly where we are at that moment in time. Opt
out of location services – unless you want the world to know exactly
where you are at all times.
3. If you wouldn’t say
something to someone in person, then don’t say it online. Be mindful of
other people’s feelings. Try and keep feelings for face to faces
encounters. Cyberbullying is no joke and what we may think might be harmless
fun may be hurtful to someone else.
4. It’s always a good idea
to regularly check your privacy settings to ensure your
details are kept private. Make sure you check who is following you and how much
of your information they can see.
5. Try to avoid posting
information that could be used to find you offline – without meaning to, you
can give away information that could help someone to find you. Don’t
give away your information, be careful of posting pictures with full
details like number plates, gig tickets with the barcodes, full addresses or
your email address.
6. Make sure your
photos and posts pass the Nana Test– if you wouldn’t show it to your
granny then it probably shouldn’t be online! Be aware that people can put
together information from photographs- a photo of your 18th birthday party can
give them your date of birth. Be careful of identifiable landmarks like street
signs near your home.
As a
teacher, you can help your students to become competent and responsible
digital citizens that can navigate the intricacies of communication now
part of the digital environment.
Educating
your students about their digital footprint and respectful online
communication will help them curate a safe social media presence.
Communication
has come a long way, there are now more ways of communicating than ever before.
Often
children know how to use newer forms of communication intuitively but we can
still provide guidance on how they can communicate, both effectively and
safely online.
In your
class, come up with a list of ways we communicate online. Here are a few
examples:
· Social networking
sites (Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram)
· Instant Messaging
Services (Messenger/Whatsapp/Viber/Snapchat)
· Video/Audio Conferencing
Services (Skype/FaceTime)
· Live streaming (Facebook,
YouTube, Netflix)
· Blogs
· Vlogs (YouTube)
· Email (Gmail, Outlook,
Yahoo, Live)
· Chatrooms
· Online Gaming (text and
audio communication)
· Forums
· Dating Sites (Tinder, PoF)
SOCIAL SHARING
Activity
#1: Social Media Use
[Before this activity, tape the “AGREE”
and “DISAGREE” signs on opposite sides of the
room. Let participants know that once you
read out each statement, they should stand
close to one side or the other depending on
how strongly they feel; participants may
also stand in the middle of the two signs if
they are unsure / undecided.]
SAY:
● I’m going to read out a statement. If you
agree one hundred percent, move to the
“AGREE” sign. If you disagree completely,
move to the “DISAGREE” sign. If
you’re unsure or don’t agree / disagree
completely, move towards the middle in a
position that best represents your view.
[In between statements, ask participants to
explain their position and engage the group
in short discussions about each topic.]
Statements / SAY:
● I have an account on a social media
platform like Facebook, Twitter, Snapchat, or
Instagram.
● I use social media every day.
● My social media profile — on the social
media platform I use the most — is
public.
● I have different friends / followers /
connections (in other words, a distinct
audience) on the various social media
platforms I use.
● My generation has a different way of
thinking about information shared on social
media platforms when compared with adults.
● I use
different social media platforms for posting specific types of content.
Activity
#2: Friend Request Spectrum
SAY:
● A social media platform is an online
platform you can use to connect with people
and interact with them.
ASK:
● What are some social media platforms
you’ve heard of?
3
[Before the following activity, tape the
“AGREE” and “DISAGREE” signs on opposite
sides of the room. Let participants know
that once you read out each statement, they
should stand close to one side or the
other depending on how strongly they feel;
participants may also stand in the middle
of the two signs if they are unsure /
undecided.]
SAY:
● I’m going to read out a statement. If
you agree one hundred percent, move to the
“AGREE” sign. If you disagree completely,
move to the “DISAGREE” sign. If
you’re unsure or don’t agree / disagree
completely, move towards the middle in a
position that best represents your view.
● For this activity, think about the
social media account you use the most.
[In between statements, engage the group
in short discussions using the questions
below each statement.]
Statements / SAY / ASK:
● My social media profile is set to
public.
○ Does this change the way you post things
online? How so? Or if not, why
not?
● My social media profile is for friends /
people I know really well only.
○ Why did you make this decision?
○ Would you post different things if
everyone could see it? What kind of
things?
● I have a friend / follower / connection
on social media whom I have never met in
real life.
○ Why did you friend / follow / connect to
this person? Was it someone you
met online, or never before?
○ How would you describe the relationship?
○ Because you solely interact online, does
it influence how you interact?
What are some of the benefits to this type
of interaction? What are
possible challenges?
● I accept every friend / follower /
connection request I get.
○ What is a benefit of this approach? What
are possible challenges?
○ Do friend / follower / connection
requests matter when it comes to your
privacy? If so, how? If not, why not?
● Whenever I meet new people, I send them
a friend / follower / connection
request.
○ Why is this a good / bad idea?
● I have deleted friends / followers /
connections.
○ Why did you make this decision?
● Online, I’m friends with / followers of
/ connected to my parents / caregivers or
teachers.
○ Does this change the way you post?
○ Do the adults in your life ever make
comments on what you post online?
○ What are possible benefits and / or
challenges of being friends / followers
of / connections with your parents /
caregivers or teachers?
● Some of the stuff on my profile can be
seen by friends of friends / people I am not
directly connected to on social media.
○ Which things?
● I have looked at and / or changed my
privacy settings.
○ Why or why not?
○ Were these privacy settings easy or
confusing? What would make these
settings
easier to view / change?
Activity
#3: How Big Is Your Network?
SAY:
● Now, let’s talk about the potential scope of your online
audience on social media.
● There are two main ways in terms of how content
(e.g., photo, video, textbased
post)
is shared with an audience. One, content can be shared with a default
audience,
which can be just your friends / followers / those you are connected to,
or
it can include friends of friends as well. Two, your initial audience can share
the
content with their friends / followers / those they are connected to.
● You can likely choose your immediate audience
but it’s
much more difficult to
control
with whom your audience reshares / reposts / retweets content.
ASK:
● Assume you share content not just with your
friends / followers / those you are
connected
to, but that the same content also gets shared with their friends /
followers
/ those they are connected to, how many people do you think you’re
sharing
with?
[Write
the following equations / results on the board.]
● Let’s do a little math. If, for example, you have two friends / followers
/
connections
on a social media platform, and each of them has three friends /
followers
/ connections, then how many people, at maximum (some friends /
followers
/ connections may probably overlap) can see the content you share on
the
platform?
○ Answer: 2 x 3 = 6
● If you have ten friends / followers /
connections on a social media platform, and
each
of them has ten friends / followers / connections, then how many people, at
maximum,
can see the content you share on the platform?
○ Answer: 10 x 10 = 100
● If you have three hundred friends / followers /
connections, and they each have
three
hundred friends / followers / connections, how many people, at maximum,
can
see the content you share on the platform?
○ Answer: 300 x 300 = 90,000
SAY:
● These calculations were based on the assumption
that your immediate audience
shares
content with their immediate audience, but no additional sharing happens
after
that. However, in many cases, content can be shared well beyond those
immediate
two audiences.
ASK:
● How do you feel about the possibility that so
many people you possibly don’t
know
(you might know some of your friends’ friends) could easily learn about
what
you do online? What might be some of the negative and / or positive
aspects
of this?
● Why does this matter?
● Does this change the way you think about
sharing things online? Why or why
not?
Activity
#4: Sharing Online
SAY:
● You may share things online for an intended
audience, but when you make
content
public, it may gain unexpected attention.
● Media shared online can go “viral,” spreading quickly over social media, being
replicated
and possibly remixed.
ASK:
● Can anyone think of an example of viral media?
[If not, ask them to think about
memes,
remixes, or popular videos they’ve seen and / or shared with their
friends.]
[Show
a recent example aligned with your / participants’ local / regional context to
further
solidify the concept.]
SAY:
● Viral media can be good if you want to draw
attention to your work. However,
unwanted
attention can potentially include harassment and bullying. A private
video
that gets leaked or shared without your permission could be damaging to
your
reputation.
ASK:
● What are some ways that content about you
online can be shared beyond your
intended
audience, and how could this potentially impact you and / or your
reputation?
VERTICAL
BASED REQUIREMENT (6 h
Digital literacy has transformed the traditional ways of imparting
education in India and around the world. In addition to how digital literacy
has impacted other areas of education sector observes
Be it in India or abroad, the first thing that digital
literacy or the internet brings on the table is the ease of gathering
information. Students in the western countries have been primarily relying on
google searches for their school assignments, in contrast to turning the pages
of outdated books that students in India do. Needless to say, gathering more
information makes the work in western countries exponentially better than in
India. What has lacked in India though, is not the intent to use technology but
the capability to use it. Not long before, not much of India had access to high
speed internet, which was overly reflected in the education system as well.
Forget about learning how to ‘google’, the course books had instructions on how
to turn a computer on. But gradually, internet is getting more accessible, not
only at schools but also at people’s houses, as it gets cheaper. Combined with
government support, cellular companies are also making internet cheaper,
resulting in a positive impact in India in terms of digital-literacy. Below are
some of the ways in which education in India, and in general, has been impacted
the most.
Communication: Students are now capable of communicating with each other
and their teachers in real time. Earlier, it was a hassle for students to
collaborate on a project. Especially during vacations, it was impossible for
them to check what the other guy is doing or to get feedback from teachers. Now
students have a number of ways to communicate, like phone calls, internet
messengers, skype etc. They can even manage work better as teachers encourage
them to use work management software like Trello and Asana.
Information gathering: Not only is the world changing, but it is changing at a
faster pace every day. Therefore, it is impossible to print the most updated
information in school books every year, and update them frequently. What can be
changed frequently though, is a web page. Internet has seen an increasing
number of students from India, looking up information related to their school
assignments. Just last year, the year-on-year growth of internet users in India
was 23%, a huge number, compared to the world average of 10%.
Online learning: With the world moving towards skill based job
opportunities, people are realising that having in-demand skills is more
important today than having a degree. Therefore, they turn to internet for
micro-courses like ‘Digital Marketing’, ‘Web Development’, etc. The number of
people paying to learn online, in India, rose from fairly none at the start of
this decade to 1.6 million in 2016, resulting from two years of 100% growth, as
per a research conducted by KPMG. Additionally, there are plenty of other
websites which provide free online courses and tutorials. An example of this
can be seen on Hackr.io which hosts links of several hundreds of websites,
which offer web development tutorials available on the internet, most of which
are free.
Career planning: With technology and automation in picture, a lot of jobs
are getting obsolete but many new ones are coming up. The challenge, however,
is to make students aware of them. Traditionally, it is parents who decide for
their children, but we all know how ineffective that is. These days, internet
is enabling students to break through the tradition. Students are now
constantly updated about what’s trending in market, through networking sites
like Linkedin and Facebook. Moreover, start-ups like iDreamCareer have come up
with online tests and counselling services, to further help the students in
making their career decisions.
Modernising schools: The most drastic change that digital brought about in
education is the technology we use at school. The most revolutionary one has
been digital boards in classrooms. This has led to students associating words
with graphics from a very early age, and is thereby improving their learning
skills. Students develop a skill of learning through videos lessons, a skill
which later manifest into them using YouTube and Khan Academy for educational
content.
Gamification of education: Not everyone learns alike, some prefer to learn by reading
in black and white, while some like to be taught through games. Digitalisation
of education brought a huge array of online games which help let children learn
easily. This also lets teachers get a thorough understanding of what a
student’s learning behaviour is like.
Showcasing talent: With internet and all the platforms it has to offer, it is
easier for students to showcase their talent and work. Students often make use
of platform like SlideShare and YouTube to publish their school assignments. A
lot of design students post their art on Dribbble and Behance, and go head on
against the professionals. This opens them up to feedback from billions of
people from the internet community and an equal chance to prove their metal.
Digital
literacy is a hot topic these days, and we’ve previously written about the
importance of it for today’s students and what teachers need to know about
helping them use technology effectively to enhance modern communication.
But although the need for digital
literacy is clear, actually teaching and using technology in educational
settings can still be a bit of a puzzle. Of course, most students are already
comfortable using a wide range of digital tools, but this doesn’t necessarily
mean they know how to use these same tools for learning purposes.
Inclusion
facilitator Dr. Kristin Bertolero from the New Jersey Coalition for Inclusive
Education (NJCIE)
frequently works with educators who need guidance on how to instruct students
in various forms of digital literacy. She notes that because technology is not
intuitive and must be learned and practiced, there’s a lot of trial and error
on the way to mastery.
“It’s easier [for teachers] to use
pre-made pencil and paper resources that they know will meet the requirements
of the assignment and earn a good grade,” says Bertolero.
“But exposure to technology,
opportunities for problem solving, and trial and error are what make someone an
expert in technology. If we can get students developing these skills at a young
age, they’ll continue to learn as the field progresses and their career
opportunities will increase astronomically.”
She points out that technology
shouldn’t be viewed as a substitute for traditional learning activities,
because although this might keep students engaged, it doesn’t help them develop
21st century problem solving skills. Instead, students should be given
opportunities to use technology to solve problems and be creative. Then,
because of their love of learning and being challenged, using technology in
their field will become an obvious continuation of their passion.
“Even if your students don’t go into
the technology industries, being able to use it and continue their own
self-directed learning can benefit them in ways we cannot presently foresee,”
she says.
Unfortunately, because digital
literacy is still one of those buzzwords that tend to get thrown around without
specifics, it can be difficult to envision what it actually means to be
digitally literate. With this in mind, we’ve rounded up some examples of what
digital literacy in education looks like.
1. Emphasise the importance of
critical thinking
The majority of media we consume
today comes from online sources, some of which are more credible than others.
Of course, the fact that so much information is readily available to anyone
with an internet connection is a decidedly positive thing. But it also means
that today’s students are more susceptible to subliminal messages,
misinformation, and fake news.
With this
in mind, a huge part of teaching digital literacy is helping students
become critical consumers of
information. Start by encouraging students to ask questions and then find
answers by going straight to the source and checking for objectivity.
2. Use social media for
learning and collaborating
Today’s students are already active
on social media, and in many cases they may already be more adept at using it
than their teachers. So the focus shouldn’t be on introducing students to the
ins and outs of social media, but on demonstrating how it can be used in an
educational context.
For example, Pinterest boards can be
used for providing and receiving feedback during group projects, Twitter can be
used create polls for research purposes or find expert sources, and Facebook or
LinkedIn groups can be used to connect and collaborate with their peers.
3. Provide guidance on how to
avoid plagiarism
Although the Internet hasn’t
necessarily made plagiarism easier, it has changed the way it happens, and
students may now be at risk of plagiarising even without meaning to. A
study published in the journal Higher Education, found that many students don’t
understand plagiarism, but they do want more information on what it is and how
to avoid it.
For example, students often ‘borrow’
ideas or use phrases they find online without properly citing the original
work, and are later surprised to learn that this constitutes plagiarism. So
another important aspect of becoming digitally literate is learning how to avoid plagiarism by
taking good notes, using citations and quotes, and properly supporting a
discussion with references.
4. Teach students to manage
their online identity
Regardless of whether we consciously
manage it or not, we all leave a digital footprint and have an online identity.
Students who have grown up using social media are more likely to take it for
granted that their data is stored online, and as a result, may not give as much
thought to safeguarding their privacy by managing their privacy settings,
reading privacy policies, and being as respectful in their online interactions
as they would be in person.
But in the
same way that not managing an online identity can have negative implications,
taking steps to build a positive one can be hugely beneficial to
students’ career prospects. With this in mind, learning how to safeguard
privacy online but also how to share the right information and content are
important aspects of a well-rounded digital literacy education.
5. Help students manage digital
distractions
Digital
tools and online resources have made learning more effective in many ways, but
they’ve also brought new distractions with them. Research shows that many of us
struggle with digital distraction, which
can make us feel distant and drained, and even reduce our enjoyment of
experiences. Juggling multiple media streams can also lead students to multi-task, which
isn’t a good thing considering that research shows that students who multi-task
tend to have lower grades.
So the ability to manage distractions
while utilising digital tools for learning and professional purposes is another
digital literacy skill that shouldn’t be overlooked. Some examples of
distraction-management strategies include taking tech breaks throughout the
day, muting notifications while studying, using productivity tools, and setting
goals around technology use.
6. Provide authentic contexts
for practice
Another
important part of teaching digital literacy is finding ways for students to
practice using technology in ways that mirror its real world uses, whether this
means giving students opportunities to practice building their own websites and
apps, or respectfully engage in online discussions.
For
example, when teaching students about the important of managing their online
identity, you could have them research themselves online to find out what a
potential employer would see. You could follow this up with a discussion about
their findings, and have them list some of the things they were proud of as
well as some of the things they’d like to change.
7. Guide students out of their
comfort zone
We all have a comfort zone when it
comes to technology, but if we want students to become innovative and
well-rounded users of technology, it’s important to guide them out of their
comfort zone whenever possible. Of course, this will mean something different
for each student.
For example, some students may
already be adept at communicating in short and distinct paragraphs and hashtags
on Twitter or Instagram, so moving out of their comfort zone might mean sharing
their opinion through a more in-depth blog post. In other cases, students might
already have experience with blogging, in which case they might be interested
in trying something a bit more out-of-the-box such as video journals or
podcasts.
Whatever the case may be, giving
students more freedom of choice and encouraging them to use technology in new
and creative ways is one of the best ways to help them hit the ground running
once they enter the workforce.
1.
Introduction
What is
important for educators and managers to consider when teaching programming,
digital design and digital literacy in secondary education? Are there didactic
methods specifically related to digital design and digital production? This
article presents a model for planning and evaluating teaching in programming,
digital design and digital literacy.
The
model was developed for secondary education in Denmark in collaboration with
teachers. The teachers were part of the ROBO learning project (2018-2020)1
which included four upper secondary schools, with most students ranging from 16
– 19 years of age, and five primary and lower secondary schools, focusing on
students ranging from 13 – 15 years of age. The upper secondary schools
encompassed general Upper Secondary School,Technical and Commercial Upper
Secondary School and Vocational Education and Training2. In addition, the model
was used to evaluate 18 of 35 courses in digital production and digital
literacy in the “crossingIT” project(2017-2019).3
The
learning perspective in this article is based on experiential, collaborative
and participatory learning processes as described by Kolb (1984), Wenger
(1998), Papert (1993), Schön (2001), Rusk et al (2008), Resnicket al (2009) and
Majgaard (2015), among others. Learning often takes place when the students
actively participate and experience new subject matter. These experiences need
to be explicitly reflected upon in the community of practice in the classroom.
2.
Didactic model for the
development and evaluation of courses
This section presents a model for evaluation
of teaching and lesson planning in programming, digital design and digital
literacy. The model can be used for exploring all the relevant aspects in the
design phases of a course and its further development. Furthermore, the model
can assist in systematically evaluating existing courses.
The model was developed in collaboration
with a selected group of teachers in the ROBOlearning project. In three
workshops and several project seminars, the teachers explained their approach
to planning and conducting teaching in digital literacy and production. They
explained their ideas in keywords and provided elaborate examples of planned
and conducted teaching in the field. In the ROBOlearning project, the teachers are
now documenting their teaching using the four elements in the model. As a
supplement, we developed questions to support and operationalise the model.
Supportive questions as well as courses can be found on the project’s website.
In the development phase, a round as well as
a linear phase model illustrating the four elements was presented to the
teachers. They preferred the round model. Learning and teaching is often circular,
iterative and complex. The round model underlines that the starting point could
be anywhere. Additionally, the model balances a technology and learning
goal-driven approach by presenting complementary approaches to didactic
planning.
3. Teaching
design
Teaching design includes common elements of
lesson planning such as learning objectives, activities, scaffolding and
practical organisation: see figure 1. In addition, the teacher must decide on
the learning output the students must produce and how it should be evaluated
(Gynther, 2010; Hiim and Hippe 2007). Traditionally, learning output includes
written texts (such as reports) and oral presentations. When the subject area
extends to IT and technology, the products become more multi-faceted and often
digitally interactive. They may include homemade computer games, digital
simulations, apps, programs, code examples, student-produced video tutorials,
robotic artefacts, video material explaining the students’ digital products,
etc. The teacher should formulate specific requirements for these digital
products (for example in games: the number of levels, start and end scenes). In
addition, the requirements can relate to a thematic framework such as, for example,
climate or future scenarios.
4. Digital
production (2)
The dimension of digital production consists
of methods for digital production, e.g. well-ordered problems, wellprepared
running codes constructed by the teacher (“worked example” Caspersen et al),
video teasers, all of which form the basis for the students' products. It is
important that the students not only copy the “worked examples”, but that the
running examples should kick-start their own further digital production. The
examplesensure that all students get a head start, avoiding some of the
frustrations and avoiding “getting stuck” from the start. There is, however,
also a risk that over-developed examples block creativity (Majgaard, 2017). In
other words, the worked examples should create a low floor and a high ceiling
(Brennan and Resnick, 2012).
1) WH of DL
13) Online payment tools usage like debit card credit card paytm
14) Online conferencing plateform usage capability like screen sharing meeting link creation , inviting other users and all
15) Bitly : URL shortning
16) Uploading files and folder and even image on Google drive and creating a sharable link also with the community
17) Usage of wetransfer link sharing
1) Web browser?
2) Search engines
3) Wiki, blogs
4) Photoshop, coral draw
6) Website and hosting
==================================================================================================================================================
After completion of this subject, you will be able to:
- Introduction to Blogs
- Basics of E-commerce
- Know the Digital Tools.
- Get Knowledge of Internet Banking Modes.
- Social Networking (Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, Instagram)
- Instant Messaging (WhatsApp, Facebook Messenger, Telegram)
- Netiquettes
- Use the Digital Locker and will be able to store documents in Digital Locker.
- E-mail Structure, Email Signature& Replying to an E-mail message
- Get familiar with eGovernance Services like Railway Reservation, Passport, eHospital [ORS], accessing e-Governance Services on Mobile Using “UMANG APP”



















































































































































































































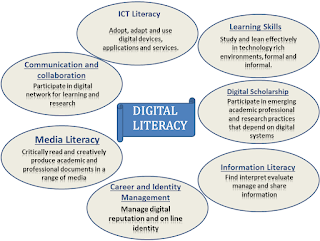



No comments:
Post a Comment
If you have any query or doubt, please let me know. I will try my level best to resolve the same at earliest.