Syllabus BCA-222
Download LP
Pedagogy
1) Handwritten Assignments-1
2) Previous year Questions Assignment-2
3) Previous year Questions Assignment-3
4) Lab File [Social media calendar - coloured]
5) PPT
6) Flip class
7) Research Paper
8) Internal Exam
9) Business plan
10) University Exam
Practice Questions for Internal Exams
2-Marks Qs. (Do any 5 Qs each Qs is of 2 marks )
1. What is Digital Marketing?
2. Discuss 4Cs of Digital Marketing?
3. Define website?
4. Write short note on SERP ?
5. What is Internet Marketing?
6. Define Digital transformation model?
7. What is SEO
5-Marks Qs. (Do any 5 Qs each Qs is of 5 marks )
8. Explain P.O.E.M framework.
9. Differentiate between Inbound and Outbound marketing?
10. Discuss the role of social media marketing in business?
11. How to apply Content marketing for a business?
12. What do you understand by Digital marketing and how is it different from conventional marketing? Explain ?
13. What is a blog? Why to create a blog?
10-Marks Qs.
(Do any One Qs each Qs is of 10 marks )
Qs 14. Discuss in detail different Social media platforms?
Qs 15. Explain different Business models?
Assignment Questions :
Hand Written Assignment Questions for BCA-222: Digital Marketing
Qs 1. Define digital marketing and explain its significance in today’s business landscape. How does it differ from traditional marketing? Research the latest trends in digital marketing (e.g., voice search, AI-driven marketing, and influencer marketing).
Qs 2. Discuss the role of Search Engine Optimization (SEO) in digital marketing. How does it impact website traffic and rankings?
Qs 3. Explain the concept of content marketing. Provide examples of how businesses use content marketing to attract and retain customers.
Qs 4. Discuss the importance of analytics tools like Google Analytics in monitoring and optimizing digital marketing campaigns.
Qs 5. Create a digital marketing strategy for a newly launched e-commerce website selling handmade jewelry. Include steps for SEO, social media marketing, and email campaigns.
Qs 6. Analyze any three digital marketing tools (e.g., HubSpot, SEMrush, Canva). Compare their features, use cases, and pricing.
Qs 7. Select a brand of your choice and evaluate its social media marketing strategy. Suggest improvements to enhance engagement and conversions.
Qs 8. Design a basic pay-per-click (PPC) campaign for a fictional local business. Define target keywords, budget, and expected outcomes.
Qs 9. Choose a global brand (e.g., Nike, Apple, or Starbucks) and examine how it uses digital marketing to maintain its brand identity across different markets.
Qs 10. Explain P.O.E.M framework.
LAB Project Work
Project-Based LAB work for BCA-222: Digital Marketing
Evaluation Criteria:
- Relevance: How well the project aligns with the specified unit objectives.
- Creativity: Innovative ideas and approaches in the project.
- Clarity: Clear and concise documentation or presentation.
- Practical Application: Real-world applicability of strategies and configurations.
- Use of Tools: Demonstration of tools like Google AdWords, Analytics, or social media platforms.
These projects will provide hands-on experience and a deeper understanding of digital marketing concepts.
Project -1: Create a presentation (10–15 slides) explaining your strategy with visuals and diagrams on topic "Designing a Digital Marketing Strategy for a Business Model"
Your presentation must include:
- Choose any business model (e.g., B2B, B2C, C2C, or
hybrid) and create a detailed digital marketing strategy for it.
- Apply the P.O.E.M framework (Paid, Owned, Earned
Media) to specify the types of platforms you would use for the strategy.
- Differentiate between Inbound and Outbound
marketing by illustrating how each can be applied to your chosen
business model.
- Develop a Digital Transformation model to
showcase how the business can adapt to digital channels.
- Identify the 4Cs of Digital Marketing (Customer, Content, Context, and Conversion) in the strategy and explain their role in achieving business goals.
Project
-2: Create a
Social Media Marketing Calender for a startup or fictional small
Sample-1 Sample-2 and Sample-3
Your
Marketing plan must include:
a)Focus on
platforms like Instagram, Snapchat, Facebook, Twitter, and Mobile marketing:
- Identify the target audience for each platform.
- Develop content ideas tailored to each platform.
- Create sample posts or mockups for at least three
platforms.
b) Suggest
platform-specific strategies (e.g., Instagram Reels for product promotion,
Facebook Ads for local targeting).
c)Include
metrics you would use to track performance (e.g., engagement rate, impressions,
CTR).
d)A
documented social media marketing plan with examples of mock posts, visuals,
and a timeline.
Project
-3: Create and Manage a Google AdWords Campaigns with each screenshots
- Develop a Google AdWords campaign for a specific
product or service of your choice (e.g., an online course, a retail store,
or a mobile app).
- Define the following:
- Campaign objective (e.g., brand awareness, lead
generation, or sales).
- Target keywords using Google Keyword Planner.
- Campaign type (e.g., Search Ads, Display Ads, Shopping
Ads, or Video Ads).
- Set a daily budget and bidding strategy.
- Create ad copies for at least three types of campaigns
with headlines and descriptions.
- Provide a mock performance report showing how you would
track key metrics like CTR, CPC, and impressions.
Project-4
: Create a sample analytics report (real
or mock data) using Google Analytics Configuration for Interpreting Google
Analytics for a Website
- Choose a real or fictional website and simulate the
configuration of Google Analytics for it.
- Define:
- The website's goals (e.g., user sign-ups, product
purchases, or content downloads).
- Conversion tracking setup (e.g., tracking form
submissions or button clicks).
- Traffic sources (e.g., direct, organic search, social
media).
- Provide a step-by-step guide on configuring Google
Analytics, including screenshots (if possible).
- Analyze a mock data report and provide insights on user
behavior, traffic sources, and areas for improvement.
.
What is Digital Marketing?
Digital marketing refers to the use of digital channels, platforms, and technologies to promote products, services, or brands to consumers. It encompasses various online strategies and tactics designed to reach targeted audiences, engage with them, and drive desired actions such as purchases, subscriptions, or website visits.
Digital marketing, on the other hand, is a broader term that includes all forms of marketing done through digital channels. This includes the internet, but also covers any kind of digital technology used for marketing purposes, such as mobile apps, display ads on digital billboards, or even digital television ads.
- Internet Marketing (SEO, email marketing, social media, etc.)
- Mobile Marketing: Promoting products or services through mobile apps, SMS, and other mobile-based channels.
- Digital Advertising: Display ads, programmatic ads, video ads, etc. on websites or apps.
- Content Marketing: Creating and distributing valuable content across different digital channels.
- Influencer Marketing: Partnering with online influencers to promote a brand, product, or service.
- Digital PR and Reputation Management: Managing and enhancing a brand's online presence through reviews, media outreach, and social listening.
Explain Key Components of Digital Marketing in detail? (10-Marks)
Search Engine Optimization (SEO):
The process of optimizing a website to rank higher on search engine results pages (SERPs) for relevant keywords, increasing organic (non-paid) traffic.
Content Marketing:
Creating and sharing valuable, relevant, and consistent content (like blogs, videos, infographics, and ebooks) to attract and retain a defined audience.
Social Media Marketing (SMM):
Using platforms like Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, and Twitter to promote products, engage with audiences, and build brand awareness.
Pay-Per-Click (PPC) Advertising:
Running paid ads on platforms like Google Ads, Bing, or social media channels. Advertisers pay only when someone clicks on their ad.
Email Marketing:
Sending targeted and personalized emails to existing or potential customers to nurture leads, inform, or promote products and services.
Affiliate Marketing:
Partnering with affiliates (individuals or companies) who promote your products in exchange for a commission on sales generated through their referrals.
Influencer Marketing:
Collaborating with influencers—people with a large following in a particular niche—to promote your brand or product.
Mobile Marketing:
Reaching customers through mobile apps, SMS, push notifications, and mobile-optimized websites.
Web Analytics and Data Analysis:
Using tools like Google Analytics to track and measure the performance of marketing campaigns, user behavior, and ROI.
Video Marketing:
Promoting products or services using video content on platforms like YouTube, TikTok, and Instagram Reels.
What is Digital Marketing? (with examples)
Digital marketing is the use of online platforms and digital technologies to market products, services, or brands. Unlike traditional marketing (e.g., TV, radio, print), digital marketing leverages tools like websites, social media, email, and search engines to connect with target audiences.
Key Components with Examples, Facts, and Figures
1. Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
SEO focuses on improving a website's visibility in search engine results.
Example:
When you search for "best smartphones under $500," brands like Samsung and OnePlus optimize their websites with relevant keywords to appear on the first page of Google.
Fact:
According to Backlinko, 68% of online experiences start with a search engine. The top 3 results on Google get 54.4% of all clicks.
2. Content Marketing
This involves creating valuable content to attract and engage audiences.
Example:
HubSpot publishes blogs and ebooks on digital marketing topics, driving traffic and generating leads.
Coca-Cola’s "Share a Coke" campaign created shareable content that users could personalize, boosting engagement.
Fact:
Content marketing costs 62% less than traditional marketing but generates 3x more leads (Demand Metric).
3. Social Media Marketing (SMM)
SMM uses platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and TikTok to reach audiences.
Example:
Nike uses Instagram for storytelling and influencer collaborations. A single post featuring an athlete often garners millions of interactions.
Burger King’s "Moldy Whopper" campaign showcased real, unedited images of their Whopper decomposing to highlight their commitment to preservative-free food.
Fact:
In 2024, there are 4.89 billion social media users, approximately 60% of the global population (Statista).
73% of marketers believe SMM has been "somewhat effective" or "very effective" for their business.
4. Pay-Per-Click (PPC) Advertising
PPC ads allow businesses to pay only when users click on their ads.
Example:
Amazon invests heavily in Google Ads to appear at the top for searches like "buy electronics."
A small business selling shoes might use Google Ads with the keyword "best running shoes," ensuring visibility.
Fact:
Businesses earn $2 for every $1 spent on Google Ads (Google Economic Impact Report).
5. Email Marketing
Sending targeted emails to potential or existing customers for promotions or engagement.
Example:
Netflix sends personalized recommendations based on user viewing history.
eCommerce sites like Amazon send cart abandonment emails to remind users of items left in their cart.
Fact:
Email marketing has an average ROI of $36 for every $1 spent (Litmus).
81% of SMBs still rely on email as their primary customer acquisition channel (Emarsys).
6. Affiliate Marketing
This is performance-based marketing where affiliates earn a commission for promoting a product.
Example:
Amazon's Affiliate Program allows bloggers and content creators to earn commissions by promoting its products.
Websites like Wirecutter earn millions in affiliate revenue through product recommendations.
Fact:
Affiliate marketing spending in the U.S. is projected to reach $8.2 billion by 2024 (Statista).
7. Influencer Marketing
Leveraging influencers to promote your brand.
Example:
Pepsi collaborated with Lionel Messi for its global campaigns.
Fitness influencers promote Gymshark apparel on platforms like Instagram and TikTok.
Fact:
89% of marketers believe ROI from influencer marketing is comparable to or better than other channels (Mediakix).
8. Mobile Marketing
Marketing campaigns designed for mobile users.
Example:
Starbucks uses its mobile app to send personalized discounts and reward notifications.
Domino’s Pizza saw a 62% increase in mobile app orders after introducing its "AnyWare" campaign.
Fact:
In 2024, 58.33% of global web traffic comes from mobile devices (Statista).
Benefits of Digital Marketing with Real-World Impact
Cost-Effective:
Small businesses with limited budgets can reach global audiences.
Example: A local bakery running a $100 Facebook ad campaign can generate leads for delivery orders.
Global Reach:
Platforms like Google Ads and YouTube enable international exposure.
Example: Shopify helps Indian artisans sell worldwide through targeted campaigns.
Measurable Results:
Tools like Google Analytics offer detailed insights.
Example: A fitness brand sees a 25% increase in sales after analyzing website traffic patterns and improving UX.
Personalization:
Tailored email campaigns boost conversion rates.
Example: Spotify Wrapped creates personalized user playlists, driving social media buzz.
Impactful Figures (2024)
Global digital marketing spend: $681 billion (Statista).
Video content drives 1200% more shares than text and images combined (WordStream).
Consumers exposed to display ads are 155% more likely to search for branded terms (Google).
Would you like insights into specific strategies or tools within digital marketing?
Digital Marketing meaning and its importance elaborate with latest updates , fact figures and examples too
Basically Digital Marketing refers to promoting products, services, or brands using digital platforms and technologies. It involves leveraging online channels like websites, search engines, email, social media, and mobile apps to reach target audiences effectively. Unlike traditional marketing, digital marketing allows real-time tracking, personalized targeting, and a global reach.
Importance of Digital Marketing
1. Global Reach and Accessibility
Digital marketing enables businesses, big or small, to connect with audiences worldwide at a fraction of the cost compared to traditional methods.
Example:
Shopify enables small businesses from rural regions to sell products globally using targeted ads on Google and Facebook.
Stat:
In 2024, global digital ad spending is projected to reach $681 billion, driven by increasing internet penetration (Statista).
2. Cost-Effective Marketing
Digital marketing campaigns cost less than TV, radio, or print ads, while providing detailed performance metrics.
Example:
A startup selling handmade crafts might invest $50 in Instagram ads and achieve sales with a targeted campaign.
HubSpot’s ROI report shows that businesses generate 3x more leads using content marketing than traditional methods.
Fact:
72% of marketers say digital marketing outperforms traditional marketing in terms of cost-effectiveness (Forbes).
3. Measurable Results
Digital marketing tools like Google Analytics, SEMrush, and Facebook Insights provide real-time data on user behavior, ROI, and campaign performance.
Example:
Amazon tracks customer interactions to optimize product suggestions, boosting sales through AI-based personalized marketing.
Fact:
Google Ads delivers a 200% ROI—businesses earn $2 for every $1 spent (Google Economic Impact Report).
4. Personalized Marketing
Digital platforms allow brands to tailor content and messaging for specific user demographics and interests.
Example:
Netflix uses AI algorithms to recommend personalized movie and series options for every user based on viewing history.
Amazon sends personalized emails reminding customers of items in their cart.
Stat:
Personalized emails increase open rates by 26% and generate 6x higher transaction rates (Campaign Monitor).
5. Enhanced Customer Engagement
Platforms like social media, chatbots, and email marketing allow businesses to engage with customers directly and build stronger relationships.
Example:
Nike engages its audience through Instagram polls, personalized ads, and influencer collaborations, driving engagement from millions of followers.
Chatbots on websites like H&M answer customer queries in real time, improving customer service.
Fact:
Social media has over 4.89 billion users globally, and 54% of users research products on social platforms before buying (Statista).
6. Improved Conversion Rates
Through retargeting ads, calls-to-action (CTAs), and optimized websites, businesses can increase sales effectively.
Example:
E-commerce brands like Myntra and Flipkart use retargeting ads to re-engage visitors who abandoned their shopping carts.
A study showed that remarketing can increase conversion rates by up to 161%.
Stat:
Websites that load faster can achieve 1.9x higher conversion rates than slow ones (Google PageSpeed).
Latest Updates in Digital Marketing
AI and Automation in Marketing
Tools like ChatGPT, Google Gemini, and HubSpot AI help businesses automate content, optimize ads, and generate leads faster.
AI-driven chatbots reduce human interaction while providing 24/7 customer support.
Example:
Coca-Cola uses AI to generate creative ad campaigns and personalized user experiences.
Voice Search Optimization
Voice assistants like Alexa, Siri, and Google Assistant are reshaping SEO strategies.
58% of consumers use voice search to find local business information (BrightLocal).
Short-Form Video Content Dominates
Platforms like TikTok, Instagram Reels, and YouTube Shorts are leading with engaging video formats.
86% of marketers say video marketing generates higher ROI (Wyzowl).
Example:
Brands like Gymshark and Samsung promote products using viral videos on TikTok.
Sustainability in Marketing
Brands are integrating eco-friendly campaigns to attract conscious consumers.
Example:
Adidas launched the "Futurecraft Loop," a fully recyclable sneaker, which gained global attention.
Key Stats and Facts for 2024
Global digital marketing industry to surpass $1 trillion by 2030 (Precedence Research).
Social media ad revenue is expected to hit $219 billion globally in 2024 (Statista).
86% of marketers believe content marketing drives more leads than traditional advertising (HubSpot).
48% of Gen Z consumers discover products via social media ads (eMarketer).
Conclusion
Digital marketing is indispensable in today’s tech-driven world. It offers businesses cost-effective, data-driven, and personalized strategies to reach global audiences, drive conversions, and enhance brand loyalty. By leveraging AI tools, video content, and social media platforms, businesses can stay competitive and adapt to evolving consumer trends.
Benefits of Digital Marketing
- Cost-Effective: Compared to traditional marketing, it often provides a better ROI.
- Global Reach: Allows businesses to reach audiences beyond geographic boundaries.
- Personalization: Enables tailored messaging to individual customer preferences.
- Real-Time Engagement: Facilitates instant communication and feedback.
- Measurable Results: Provides detailed metrics for tracking campaign success.
- Applications of Digital Marketing
Digital marketing is widely used across industries, including e-commerce, education, healthcare, real estate, and more. With the rise of AI tools and advanced analytics, it continues to evolve, offering innovative ways to connect with audiences
📘 1. What is Digital Marketing
Digital marketing refers to:
- Marketing through newspapers
- Marketing using digital channels and technologies
- Marketing only via radio
- Marketing through billboards
Answer: b) Marketing using digital channels and technologies
Which of the following is NOT a digital marketing channel?
- SEO
- PPC
- Social Media
- Flyers
Answer: d) Flyers
2. Components of Digital Marketing
Which of these is a major component of digital marketing?
- SEO
- PPC
- Content Marketing
- All of the above
Answer: d) All of the above
Email marketing is mainly used for:
- Customer retention and engagement
- Outdoor advertising
- Search engine ranking
- None of the above
Answer: a) Customer retention and engagement
3. Demographics
In digital marketing, demographics usually include:
- Age, gender, income, education
- Weather conditions
- Road traffic
- None of the above
Answer: a) Age, gender, income, education
Why are demographics important in digital marketing?
- To design better websites
- To target the right audience
- To reduce printing costs
- To increase offline sales only
Answer: b) To target the right audience
4. ROI (Return on Investment)
ROI in digital marketing measures:
- The number of likes on a post
- The profitability of campaigns
- The cost of printing brochures
- The number of offline customers
Answer: b) The profitability of campaigns
Which formula is commonly used for ROI?
- (Gain – Cost) ÷ Cost
- Cost ÷ Gain
- Gain × Cost
- None of the above
Answer: a) (Gain – Cost) ÷ Cost
5. PPC (Pay-Per-Click)
In PPC advertising, the advertiser pays:
- For every impression
- For every click
- For every offline sale
- For every flyer distributed
Answer: b) For every click
Which platform is most popular for PPC campaigns?
- Google Ads
- Facebook Groups
- TV commercials
- Newspaper ads
Answer: a) Google Ads
📘1. What is Digital Marketing
Digital marketing refers to:
- Marketing through newspapers
- Marketing using digital channels and technologies
- Marketing only via radio
- Marketing through billboards
Answer: b
Which of the following is NOT a digital marketing channel?
- SEO
- PPC
- Social Media
- Flyers
Answer: d
Digital marketing differs from traditional marketing because:
- It is offline only
- It uses digital tools and analytics
- It avoids customer engagement
- It is less measurable
Answer: b
The main goal of digital marketing is:
- Entertainment
- Customer engagement and conversions
- Printing brochures
- Offline sales only
Answer: b
Which is a digital marketing strategy?
- SEO
- Flyers
- Billboards
- Pamphlets
Answer: a
Digital marketing allows:
- Real-time tracking
- Limited reach
- No interaction
- Only offline campaigns
Answer: a
Which of these is a key advantage of digital marketing?
- High printing cost
- Global reach
- Limited audience
- No analytics
Answer: b
Digital marketing is also known as:
- Online marketing
- Offline marketing
- Traditional marketing
- Print marketing
Answer: a
Which of these is NOT part of digital marketing?
- SEO
- PPC
- Social Media Marketing
- Door-to-door sales
Answer: d
Digital marketing is most effective because:
- It is measurable and targeted
- It is random
- It is offline only
- It avoids customer data
Answer: a
2. Components of Digital Marketing
- Which of these is a major component of digital marketing?
- SEO
- PPC
- Content Marketing
- All of the above
Answer: d
- Email marketing is mainly used for:
- Customer retention and engagement
- Outdoor advertising
- Search engine ranking
- None of the above
Answer: a
- Which of these is NOT a digital marketing component?
- Social Media Marketing
- Search Engine Optimization
- Radio Advertising
- Pay-Per-Click
Answer: c
- Content marketing focuses on:
- Creating valuable, relevant content
- Printing flyers
- Door-to-door sales
- None of the above
Answer: a
- SEO stands for:
- Search Engine Optimization
- Social Engagement Outreach
- Sales Enhancement Operation
- None of the above
Answer: a
- PPC stands for:
- Pay-Per-Click
- Print-Paper-Cost
- Public Promotion Campaign
- None of the above
Answer: a
- SEM is a combination of:
- SEO + PPC
- Flyers + Billboards
- Radio + TV Ads
- None of the above
Answer: a
- Social Media Marketing involves:
- Promoting via Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn
- Distributing pamphlets
- Running TV ads
- None of the above
Answer: a
- Analytics in digital marketing helps in:
- Measuring campaign performance
- Printing costs
- Offline distribution
- None of the above
Answer: a
- Which of these is a paid digital marketing method?
- PPC
- SEO
- Content Marketing
- Blogging
Answer: a
3. Demographics in Digital Marketing
- Demographics in marketing refers to:
- Customer lifestyle choices
- Statistical data about populations
- Weather conditions
- Road traffic patterns
Answer: b
- Which of the following is NOT a demographic factor?
- Age
- Gender
- Income
- Website speed
Answer: d
- Why are demographics important in digital marketing?
- To target the right audience
- To reduce printing costs
- To design better websites only
- To increase offline sales only
Answer: a
- A campaign targeting “18–24 year olds” is based on:
- Geographic segmentation
- Demographic segmentation
- Behavioral segmentation
- Psychographic segmentation
Answer: b
- Which demographic factor is most useful for luxury product marketing?
- Income level
- Weather condition
- Traffic congestion
- None of the above
Answer: a
- Gender-based targeting is an example of:
- Demographic segmentation
- Geographic segmentation
- Behavioral segmentation
- None of the above
Answer: a
- Education level is considered a:
- Demographic factor
- Geographic factor
- Behavioral factor
- None of the above
Answer: a
- Which of these platforms allows demographic targeting?
- Facebook Ads Manager
- Google Ads
- LinkedIn Ads
- All of the above
Answer: d
- Demographics help marketers to:
- Personalize campaigns
- Increase relevance
- Improve ROI
- All of the above
Answer: d
- Targeting based on marital status is an example of:
- Demographic segmentation
- Geographic segmentation
- Behavioral segmentation
- None of the above
Answer: a
4. ROI in Digital Marketing (Q31–40)
- ROI stands for:
- Return on Investment
- Rate of Interest
- Revenue on Internet
- None of the above
Answer: a
- ROI in digital marketing measures:
- Profitability of campaigns
- Number of likes only
- Printing costs
- Offline distribution
Answer: a
- Which formula is commonly used for ROI?
- (Gain – Cost) ÷ Cost
- Cost ÷ Gain
- Gain × Cost
- None of the above
Answer: a
- A positive ROI means:
- Campaign is profitable
- Campaign is loss-making
- Campaign has no effect
- None of the above
Answer: a
- ROI helps marketers to:
- Measure success of campaigns
- Reduce costs
- Improve strategies
- All of the above
Answer: d
- Which metric is NOT directly linked to ROI?
- Conversion rate
- Customer acquisition cost
- Bounce rate
- Weather condition
Answer: d
- ROI is important because:
- It shows profitability
- It helps allocate budget
- It improves decision-making
- All of the above
Answer: d
- If a campaign cost $1000 and generated $3000 revenue, ROI is:
- 200%
- 100%
- 300%
- None of the above
Answer: a
- ROI analysis helps in:
- Identifying effective channels
- Cutting ineffective campaigns
- Improving future strategies
- All of the above
Answer: d
- Which of these tools helps measure ROI in digital marketing?
- Google Analytics
- Facebook Insights
- HubSpot
- All of the above
Answer: d
📘5. PPC (Pay-Per-Click) (Q41–50)
- In PPC advertising, the advertiser pays:
- For every impression
- For every click
- For every offline sale
- For every flyer distributed
Answer: b
- Which platform is most popular for PPC campaigns?
- Google Ads
- Facebook Groups
- TV commercials
- Newspaper ads
Answer: a
- PPC is considered a:
- Paid marketing strategy
- Free marketing strategy
- Offline marketing strategy
- None of the above
Answer: a
- Which metric is most important in PPC campaigns?
- Click-Through Rate (CTR)
- Printing cost
- Offline distribution
- None of the above
Answer: a
- PPC campaigns are usually charged on:
- Cost per click (CPC)
- Cost per impression (CPM)
- Cost per acquisition (CPA)
- All of the above
Answer: d
- Which of these is NOT a PPC platform?
- Google Ads
- Bing Ads
- Instagram Ads
- Door-to-door sales
Answer: d
- PPC campaigns allow:
- Targeting specific keywords
- Tracking conversions
- Budget control
- All of the above
Answer: d
- A high Quality Score in Google Ads means:
- Better ad relevance and lower CPC
- Higher printing costs
- More offline reach
- None of the above
Answer: a
- Which of these affects PPC performance?
- Ad relevance
- Landing page quality
- Keyword selection
- All of the above
Answer: d
- PPC is best suited for:
- Immediate traffic generation
- Long-term organic ranking
- Offline sales
- None of the above
Answer: a
6. SEO (Search Engine Optimization) (Q51–60)
- SEO stands for:
- Search Engine Optimization
- Social Engagement Outreach
- Sales Enhancement Operation
- None of the above
Answer: a
- The main goal of SEO is:
- Improve website visibility in search engines
- Increase offline sales
- Print more brochures
- None of the above
Answer: a
- Which of these is NOT part of SEO?
- On-page optimization
- Off-page optimization
- Technical SEO
- Door-to-door sales
Answer: d
- On-page SEO includes:
- Title tags and meta descriptions
- Keyword optimization
- Internal linking
- All of the above
Answer: d
- Off-page SEO mainly focuses on:
- Backlinks and domain authority
- Printing flyers
- Website design only
- None of the above
Answer: a
- Technical SEO involves:
- Website speed and mobile-friendliness
- Keyword stuffing
- Flyer distribution
- None of the above
Answer: a
- Which tool is commonly used for SEO analysis?
- Google Search Console
- SEMrush
- Ahrefs
- All of the above
Answer: d
- Keywords in SEO are important because:
- They help search engines understand content
- They reduce printing costs
- They increase offline distribution
- None of the above
Answer: a
- Which factor affects SEO ranking?
- Page load speed
- Mobile responsiveness
- Quality content
- All of the above
Answer: d
- SEO is considered a:
- Long-term strategy
- Short-term paid strategy
- Offline marketing strategy
- None of the above
Answer: a
📘 7. Social Media Marketing (SMM) (Q61–70)
- Social Media Marketing involves:
- Promoting via Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn
- Distributing pamphlets
- Running TV ads
- None of the above
Answer: a
- Which of these is NOT a social media platform?
- Twitter (X)
- Radio FM
Answer: d
- The main benefit of SMM is:
- Direct engagement with customers
- Offline distribution
- Printing brochures
- None of the above
Answer: a
- Which metric is commonly used in SMM?
- Likes, shares, comments
- Printing cost
- Road traffic
- None of the above
Answer: a
- Influencer marketing is part of:
- Social Media Marketing
- SEO
- PPC
- None of the above
Answer: a
- Which platform is best for professional networking?
- TikTok
- Snapchat
Answer: a
- A “viral campaign” usually refers to:
- Rapid spread of content on social media
- Offline distribution
- Printing flyers
- None of the above
Answer: a
- Social media ads can be targeted based on:
- Demographics
- Interests
- Behavior
- All of the above
Answer: d
- Which of these is a paid SMM strategy?
- Facebook Ads
- Instagram Ads
- LinkedIn Ads
- All of the above
Answer: d
- SMM is effective because:
- It builds brand awareness and engagement
- It reduces printing costs
- It avoids customer interaction
- None of the above
Answer: a
8. Search Engine Marketing (SEM) (Q71–80)
- SEM stands for:
- Search Engine Marketing
- Social Engagement Media
- Sales Enhancement Method
- None of the above
Answer: a
- SEM is a combination of:
- SEO + PPC
- Flyers + Billboards
- Radio + TV Ads
- None of the above
Answer: a
- Which of these is a paid SEM strategy?
- PPC
- SEO
- Blogging
- None of the above
Answer: a
- SEM campaigns are usually run on:
- Google Ads
- Bing Ads
- Yahoo Ads
- All of the above
Answer: d
- The main goal of SEM is:
- Increase visibility in search engines
- Print more flyers
- Increase offline distribution
- None of the above
Answer: a
- Which metric is important in SEM?
- Click-Through Rate (CTR)
- Conversion Rate
- Cost per Acquisition (CPA)
- All of the above
Answer: d
- SEM differs from SEO because:
- SEM includes paid strategies
- SEM is offline only
- SEM avoids keywords
- None of the above
Answer: a
- Which of these is NOT part of SEM?
- PPC
- SEO
- Flyers
- None of the above
Answer: c
- SEM campaigns can be targeted based on:
- Keywords
- Location
- Demographics
- All of the above
Answer: d
- SEM is effective because:
- It provides immediate visibility and measurable results
- It reduces printing costs
- It avoids customer engagement
- None of the above
Answer: a
📘 9. Benefits of Digital Marketing (Q81–90)
- Which of these is a key benefit of digital marketing?
- Global reach
- Limited audience
- High printing cost
- None of the above
Answer: a
- Digital marketing is cost-effective because:
- It reduces printing and distribution costs
- It requires only offline campaigns
- It avoids customer engagement
- None of the above
Answer: a
- Which of these benefits is unique to digital marketing?
- Real-time analytics
- Flyers distribution
- TV commercials
- None of the above
Answer: a
- Digital marketing helps in:
- Building brand awareness
- Customer engagement
- Lead generation
- All of the above
Answer: d
- Which of these is NOT a benefit of digital marketing?
- Measurable results
- Targeted campaigns
- Offline-only reach
- Cost-effectiveness
Answer: c
- Digital marketing allows personalization by:
- Using customer data for tailored campaigns
- Printing more flyers
- Broadcasting random ads
- None of the above
Answer: a
- Which of these is a benefit of SEO in digital marketing?
- Long-term visibility
- Paid traffic only
- Offline distribution
- None of the above
Answer: a
- Social media marketing benefits brands by:
- Increasing engagement and loyalty
- Reducing printing costs
- Avoiding customer interaction
- None of the above
Answer: a
- PPC campaigns benefit businesses by:
- Driving immediate traffic
- Improving offline reach
- Printing brochures
- None of the above
Answer: a
- Digital marketing benefits small businesses because:
- It provides affordable visibility
- It requires huge budgets only
- It avoids analytics
- None of the above
Answer: a
10. Mixed Practice (Q91–100)
- Which of these is a digital marketing channel?
- SEO
- PPC
- Social Media
- All of the above
Answer: d
- ROI stands for:
- Return on Investment
- Rate of Interest
- Revenue on Internet
- None of the above
Answer: a
- Which of these is NOT a demographic factor?
- Age
- Gender
- Weather condition
- Income
Answer: c
- SEM is a combination of:
- SEO + PPC
- Flyers + Billboards
- Radio + TV Ads
- None of the above
Answer: a
- Which of these tools is used for SEO?
- Google Search Console
- SEMrush
- Ahrefs
- All of the above
Answer: d
- PPC campaigns are charged on:
- CPC, CPM, CPA
- Printing cost
- Offline distribution
- None of the above
Answer: a
- Social media metrics include:
- Likes, shares, comments
- Printing cost
- Road traffic
- None of the above
Answer: a
- Which of these is a benefit of digital marketing?
- Measurable results
- Targeted campaigns
- Cost-effectiveness
- All of the above
Answer: d
- Which of these is NOT part of digital marketing?
- SEO
- PPC
- Flyers
- Social Media Marketing
Answer: c
- Digital marketing is effective because:
- It is measurable, targeted, and scalable
- It is random
- It is offline only
- It avoids customer data
Answer: a
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO): Optimizing content and websites to rank higher in search engine results.
- Email Marketing: Sending targeted emails to a list of subscribers to nurture relationships and drive conversions.
- Social Media Marketing: Using platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter to engage with customers and promote content.
- Affiliate Marketing: Partnering with affiliates to promote products in exchange for a commission on sales or leads.
- Pay-Per-Click (PPC) Advertising: Paying for ads that appear in search engines, social media, or other websites, where you pay based on clicks.
Internet Marketing: It is a subset of digital marketing that specifically focuses on activities that use the internet to market products and services. This includes SEO, online advertising, email marketing, and affiliate marketing that are conducted through the internet.Digital Marketing: Digital marketing is a broader term that covers not only internet marketing, but also marketing activities that involve digital technologies beyond the internet, such as mobile apps, SMS marketing, and digital signage.
Internet Marketing: Channels include websites, search engines, email, social media, and online ads. Essentially, anything that occurs exclusively online is considered part of internet marketing.Digital Marketing: This covers all digital channels, both online and offline. For example, it includes the internet, but also includes mobile marketing, digital TV ads, SMS marketing, and digital billboards.Technology:Internet Marketing: Relies solely on the internet as the primary medium for connecting with the target audience. This means it focuses on internet-specific tools and technologies.Digital Marketing: Encompasses both online and offline channels, including mobile technologies, digital media, wearables, and even interactive TV ads, alongside internet-based tools.
What is POEM Framework in Digital marketing startegy
The POEM Framework in digital marketing is a model used to categorize the various digital marketing channels and approaches based on control, ownership, and earned visibility. The POEM framework helps businesses understand the different types of media they can use to communicate with their audience and how to effectively allocate their marketing resources.
The POEM framework is divided into three key components:
1. Paid Media
Definition: Paid media refers to any form of digital marketing where the business pays for exposure or visibility. It includes advertisements and other paid placements on platforms where the company doesn’t own the media space.
Examples:
- Search Engine Ads (e.g., Google Ads)
- Social Media Ads (e.g., Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn ads)
- Display Ads (e.g., banner ads on websites)
- Affiliate Marketing (Paying affiliates for driving traffic or sales)
Benefits: Immediate reach, targeting capabilities, scalability, and measurable results.
Challenges:
High costs (especially in competitive industries), dependency on platforms, ad fatigue.
2. Owned Media
Definition: Owned media refers to the digital assets that a business owns and controls. These are platforms or channels that are directly managed by the company, where they have full control over content, design, and messaging.
Examples:
- Website (Corporate site, e-commerce site, landing pages)
- Blog (Content creation and distribution)
- Social Media Accounts (Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn pages)
- Email Lists (Newsletters and direct email campaigns)
- Mobile Apps (Proprietary apps for business)
Benefits: Full control over content and branding, long-term value, cost-effective once set up.
Challenges: Requires time, effort, and investment to grow and maintain. Building an audience takes time.
3. Earned Media
Definition: Earned media refers to the publicity a business gains through organic efforts, usually in the form of customer interactions, social shares, media coverage, or word-of-mouth. It's the type of media you "earn" through excellent products, services, or content.
Examples:
- Organic Search (SEO results)
- Social Media Shares (User-generated content, retweets, and shares)
- Online Reviews (Customer testimonials on platforms like Yelp or Google Reviews)
- Public Relations (Mentions in articles, news features, interviews)
- Influencer Recommendations (When influencers or brand advocates talk about your product without being paid directly for it)
Benefits: Builds trust and credibility, cost-effective, sustainable in the long term.
Challenges: Hard to control and predict, dependent on external factors like audience engagement, press coverage, or customer reviews.
Why is POEM Framework Important in Digital Marketing?
The POEM Framework provides a balanced approach to a business's marketing efforts. By understanding and leveraging all three categories (Paid, Owned, and Earned), businesses can create a more well-rounded digital marketing strategy. Here’s how the POEM framework contributes to a comprehensive marketing strategy:
Diversity in Channels: It ensures that marketers aren't putting all their efforts into one channel but are diversifying across paid, owned, and earned media to reach audiences at various touchpoints.
Synergy: By combining paid, owned, and earned media, companies can amplify their message. For example, paid ads can drive traffic to your owned media (like a blog), and if the content is valuable, it can lead to earned media (organic social shares and mentions).
Cost-Effectiveness: Paid media might bring instant results but is often costly. Owned media (like a website or email list) provides a more sustainable long-term solution, while earned media often leads to free publicity and credibility.
Improved Customer Journey: A well-rounded strategy using POEM ensures that the brand has touchpoints with potential customers at all stages of the buying journey — from awareness (through paid ads) to consideration (via owned media like informative content) and finally to loyalty and advocacy (through earned media like positive reviews or social mentions).
How to Apply the POEM Framework in Digital Marketing Strategy?
Assessment of Current Channels:
Evaluate what types of media your business is currently using. Do you rely mostly on paid ads? Or do you have an extensive blog and active social media accounts that you own? What types of earned media do you already have (e.g., positive reviews, organic search traffic)?
Integration:
Use Paid Media to create immediate brand awareness and drive traffic.
Use Owned Media (website, email, social profiles) to build relationships and establish long-term customer loyalty.
Encourage Earned Media by creating shareable content and providing an excellent customer experience, which motivates customers to talk about your brand.
Continuous Optimization:
Measure the performance of each type of media (Paid, Owned, Earned). Paid media can be optimized with A/B testing, Owned media can be updated for better user experience, and Earned media can be leveraged through engagement and PR strategies.
Strategy Balance:
Balance how much effort and investment you dedicate to each category. Too much focus on paid media without nurturing owned and earned channels can lead to higher costs. On the other hand, relying solely on earned media may take longer to yield results.
Example of POEM Framework in Action
Let’s consider an example of a fitness brand using the POEM framework:
Paid Media:
Run Google Ads and Facebook ads to target people searching for fitness solutions.
Use Instagram Ads to promote new workout programs or offers.
Owned Media:
The brand’s website where customers can sign up for online classes and purchase products.
Maintain a blog that provides fitness tips, guides, and success stories.
An email list that sends workout tips, promotional offers, and newsletters.
Earned Media:
Customers leaving positive reviews on the fitness program’s website or third-party platforms.
Followers sharing workout content on social media (Instagram, Twitter).
Influencers organically mentioning the brand in their posts or videos.
By combining Paid Media for immediate traffic, Owned Media for long-term engagement, and Earned Media to build trust and authority, the fitness brand can create a robust and effective digital marketing strategy.
Conclusion
The POEM framework is an essential tool for creating a comprehensive, balanced digital marketing strategy. By understanding how Paid, Owned, and Earned Media interact and contribute to different aspects of customer engagement, businesses can more effectively allocate resources, reduce dependency on one particular channel, and build a sustainable marketing ecosystem. Whether you're a small business or a large enterprise, the POEM framework helps ensure that you're targeting your audience through the right mix of channels.
Here are some facts, figures, and examples that showcase how the POEM (Paid, Owned, Earned Media) framework works in practice and its impact on digital marketing strategies.
1. Paid Media Facts and Figures
Paid media is often one of the quickest ways to drive traffic and visibility to your brand, but it can also be costly. Below are some stats and examples to highlight its importance and effectiveness:
Facts and Figures:
Google Ads:
Google Ads has over 2 million active advertisers worldwide as of 2023. (Source: Google)
Businesses make an average of $8 for every $1 spent on Google Ads. (Source: Google Economic Impact Report)
Social Media Advertising:
Facebook Ads have a potential reach of 2.96 billion users (Source: Statista, 2023).
The average Cost-Per-Click (CPC) for Facebook Ads in 2023 was approximately $1.72 (Source: WordStream).
In 2023, Instagram Ads generate $27.64 billion in ad revenue annually. (Source: Statista)
Example:
Example of Paid Media:
A fashion brand running Facebook and Instagram ads targeting fashion-conscious individuals aged 18-35, showcasing a limited-time discount. The ads are shown to 500,000 users, driving 15,000 clicks to the website. If the average cost-per-click (CPC) is $1.50, the brand will spend $22,500 but might generate significant sales from those 15,000 visitors.
2. Owned Media Facts and Figures
Owned media is critical for creating long-term customer relationships and maintaining control over your brand messaging. Let’s look at some statistics:
Facts and Figures:
Website Traffic:
61% of mobile searchers are more likely to contact a business whose website or landing page is mobile-friendly. (Source: Google)
Companies with a blog receive 55% more website traffic than those without one. (Source: HubSpot)
On average, businesses see a 2-5% conversion rate from their websites. (Source: Invesp)
Email Marketing:
For every $1 spent on email marketing, businesses see an average return of $42. (Source: DMA, 2019)
Email open rates are higher in industries like e-commerce (18-25%) compared to others like B2B or non-profit (Source: Campaign Monitor).
Transactional emails (order confirmations, receipts, etc.) have 8x higher open rates than regular promotional emails. (Source: Omnisend)
Example:
Example of Owned Media:
An e-commerce store has a blog where it posts SEO-optimized articles about product usage, fashion trends, and style tips. Over the course of 6 months, these articles help increase organic traffic by 30%, resulting in 15,000 new visitors per month to the website. Additionally, the brand has an email list of 50,000 subscribers that regularly receives newsletters about new arrivals and exclusive discounts.
3. Earned Media Facts and Figures
Earned media is a powerful component of a digital marketing strategy, as it’s based on organic, unpaid exposure. Let’s explore some interesting facts and figures:
Facts and Figures:
Online Reviews:
93% of consumers read online reviews before making a purchase decision. (Source: Spiegel Research Center)
Positive reviews can increase conversion rates by 270%. (Source: Invesp)
50% of consumers say they trust online reviews just as much as personal recommendations. (Source: BrightLocal)
Social Media:
92% of consumers trust recommendations from peers and family over any other form of advertising. This includes social media mentions and shares. (Source: Nielsen)
Twitter mentions can lead to a 30% increase in conversion rates when accompanied by positive reviews or customer-generated content. (Source: Sprout Social)
Example:
Example of Earned Media:
A hotel brand receives positive reviews on platforms like TripAdvisor, leading to higher rankings and more visibility. Over time, the brand builds a reputation through social media shares and word-of-mouth recommendations, gaining 100,000 social media followers and increasing organic traffic by 40%. This earned attention helps boost the hotel’s bookings without any additional ad spend.
POEM Framework Example for a Fashion Brand
Let’s put the POEM framework into action using a fashion brand as an example:
Paid Media:
The brand runs Google Search Ads targeting keywords like “best summer dresses 2025” and Instagram Ads showcasing influencer partnerships and new arrivals. These ads generate 50,000 impressions and 3,000 clicks to the brand's landing page.
Results: The brand spends $10,000 on paid ads and generates $35,000 in sales.
Owned Media:
The fashion brand has a blog where it regularly posts articles about styling tips, seasonal trends, and fashion guides. These articles rank for organic keywords like “summer fashion trends” and drive 30% more organic traffic to the website.
The brand also sends weekly email newsletters to 25,000 subscribers, promoting exclusive discounts and new arrivals, leading to higher engagement and repeat purchases.
Earned Media:
The brand’s Instagram followers (now 100,000 followers) start posting about their purchases using branded hashtags, leading to more social shares and engagement.
Influencers start sharing unboxing videos, increasing brand awareness. PR coverage from popular fashion blogs mentions the brand as a top pick for summer 2025 trends.
Impact of POEM:
The combination of Paid Media for immediate reach, Owned Media for long-term customer relationships, and Earned Media for organic trust and advocacy creates a comprehensive digital marketing strategy. This leads to not just immediate sales but also brand loyalty, organic growth, and community-building.
Key Takeaways
Paid Media allows for quick, targeted visibility but can be expensive. It's essential for driving immediate traffic, and with proper management, it can be a scalable source of leads.
Owned Media provides long-term value and control, helping to build customer loyalty, brand identity, and a reliable source of traffic. It’s important for developing a sustainable digital presence.
Earned Media is the most cost-effective form of marketing because it is based on the trust and advocacy generated by customers and the press. It helps build credibility and long-term success.
By combining Paid, Owned, and Earned Media, brands can create a holistic and balanced digital marketing strategy that reaches customers at multiple touchpoints, drives traffic, and fosters long-term growth.
What is Inbound marketing?
Inbound marketing is focused on attracting customers to your products and services. Your best prospects are searching for products online, with up to 63% of consumers starting their shopping journey online.
They begin by searching for products and services, or content to fulfill a need and solve a problem. As such, your content should explain how your products or services will resolve their issues, answer key questions in their niche industry, or satisfy their needs.
There are many ways to do this, including:
- Blogs
- Video content
- Guidebooks
- Other online marketing content
Each of these content pieces can also serve as a way to differentiate your product from the competition. Embed product comparisons, amazing testimonials, competitive pricing, and outstanding reviews into your podcast, social media posts, or reports.
Keep in mind that prospective customers should receive thoughtful content at various points throughout their buying journey, that is varied in material, but consistent in messaging.
Inbound marketing strategy aims to gently nurture potential customers through the marketing funnel, exposing them to relevant content and brand experiences when they are ready, gradually building brand awareness, increasing customer engagement, and pulling them towards conversion and retention. This is how the inbound funnel works
An example of inbound marketing.
Let’s say a customer is looking for a new marketing software. First, they may type “best marketing tool” into a search engine, to explore the landscape.
The first organic result may be a blog outlining the top 10 marketing platforms in a clear, unbiased way. After reading the post, they might want to learn more about digital marketing.
Conveniently, the end of the blog has a link to encourage them to sign up for an upcoming webinar, to learn more about a new digital marketing strategy. They click the link, then enter their name and email address to access the content. The site then stores their contact information and tracks whether or not they attend the webinar.
Once they attend the webinar, they might wonder if any companies successfully implemented the strategy that was discussed. Right on cue, the vendor will send them a follow-up email, containing case studies that show how one of their competitors effectively used digital marketing to achieve a huge ROI.
This prompts them to request a demo with a sales representative. They go into the sales call already interested in (and educated on) what the software does, providing you with an easier sell.
Benefits of inbound marketing.
- There are several benefits to inbound marketing that can help you determine if it’s the right strategy for your company:
- Inbound marketing is non-invasive. Prospects can read your blog posts or attend a webinar on their own time.
- Inbound marketing content is educational. It is specifically designed for each stage in the sales funnel.
- Inbound marketing is quantifiable. You can tie each part of your strategy to a metric that gets monitored over time.
- Your website and content are continuously being updated, so inbound marketing continues generating leads over time.
Challenges of inbound marketing.
Of course, inbound marketing isn’t for every company. There are some drawbacks to focusing solely on digital content.
Inbound marketing:
- Requires continuous maintenance. This is to ensure that content always speaks to consumers’ evolving wants and needs.
- Takes a great deal of time and effort. Developing and testing out different content that will entice customers to convert takes time.
- Demands a holistic strategy. You’ll need to buy tools to help you implement integrated, cross-channel campaigns.
What is outbound marketing?
Outbound marketing sends a message to a huge amount of people, in the hopes of making a sale. This strategy is rooted in the thought that the larger the group you message to, the larger the return.
Outbound marketing is often associated with traditional marketing, like:However, outbound marketing can also be applied to more modern technology, like pay-per-click advertising and spam emails.
- Direct mail
- Events
- Billboards
- Cold calling
- Newspapers
- Radio
- TV
Frequently, consumers are not even aware of or looking for the product that’s being advertised. Prospects could be watching TV or perusing a website and be interrupted by an ad illustrating why they should buy a certain product.
An example of outbound marketing.
A customer is driving on the highway and sees a billboard for a furniture store in the area. They might briefly think that they really should invest in a new couch, but they keep that in the back of their mind.
A few weeks later, as they watch the local news, they see a commercial for the same furniture store. Again, they think about buying a couch, but forget after the news comes back on.
Three months later, they check their mailbox and find a discount coupon for the furniture store. As it happens, they just received a bonus at work. Finally, they decide to go ahead and buy that new couch.
None of the ads referred to a couch, and they weren’t necessarily looking to buy one right away. Nevertheless, ads kept popping up in their everyday life, so they ended up shifting their attention to a need that wasn’t top of their mind initially.
Benefits of outbound marketing.
- Outbound marketing has a few perks that should not be overlooked.
- Outbound marketing:Promotes brand awareness. Reach people who haven’t heard of your products or services before.Can yield immediate results. People interested in your products and services are likely to take action on your ads and make a purchase.
- Is something consumers are used to. They know that there will be ads in the Sunday paper or on TV and may trust those ads more than the ones presented to them on newer technology.
Challenges of outbound marketing.
- Outbound marketing can be difficult to get right. Here are some disadvantages of going along this route:
- Outbound marketing is more generalized. It’s difficult to make outbound marketing appealing and relevant to everyone.
- It’s easy for consumers to tune out outbound marketing. Many people mute the TV during commercials or immediately throw out or recycle their junk mail.
- Measuring the effectiveness is harder. It’s challenging to measure results of some outbound marketing strategies like billboards.
- Outbound marketing is costly. Traveling to trade shows, paying for banner ads, and purchasing billboard spaces add up.
- Overall, outbound marketing is all about sending a message at scale, while inbound marketing has a very targeted approach.
The likelihood that at least some people will convert from your outbound marketing efforts is high, but it is often associated with a high acquisition cost.
Rather than shouting your product’s name from the rooftops and hoping that a few people respond, inbound marketing content can be finely tuned to appeal to your best-fit prospects.
The difference between inbound and outbound marketing.
There are several main differences between inbound and outbound marketing. Outbound marketing involves proactively reaching out to consumers to get them interested in a product. By contrast, inbound marketing centers on creating and distributing content that draws people into your website.
Outbound marketing typically has a more aggressive, wide-sweeping approach, with the expectation that at least some people will convert. Inbound marketing is usually more subtle and focuses on convincing a particular group of individuals to make a purchase over time.
Explore
https://www.ionology.com/wp-new/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/DTinpractice-1024x577.jpg
A Digital transformation model in marketing refers to a strategic framework that guides a company in fundamentally changing its marketing practices by leveraging digital technologies to improve customer engagement, optimize operations, and deliver a more personalized customer experience across all digital channels, often requiring a shift in company culture and mindset to embrace digital innovation fully.
Key aspects of a digital transformation model in marketing:
Customer-centric approach:
Prioritizing understanding customer needs and behaviors through data analysis to tailor marketing strategies accordingly.Multi-channel marketing:
Utilizing a variety of digital channels like social media, email, search engine optimization (SEO), pay-per-click (PPC) advertising, and content marketing to reach customers where they are.Data-driven decision making:
Using customer data to inform marketing decisions, track campaign performance, and make adjustments based on real-time insights.Personalization:
Delivering customized content and experiences to individual customers based on their preferences and behavior.Agile methodology:
Continuously iterating and adapting marketing strategies based on customer feedback and evolving digital landscape.
Examples of digital transformation in marketing:
Implementing a CRM system:
To manage customer interactions and provide a unified view of customer data across channels.
Developing a personalized website experience:
Tailoring content and product recommendations based on user behavior and demographics.
Leveraging social media analytics:
Tracking customer sentiment and engagement on social platforms to refine marketing strategies.
Utilizing marketing automation tools:
Automating repetitive marketing tasks like email sequences and lead nurturing.
Important considerations when implementing a digital transformation model:
Leadership commitment:
Top management needs to champion the digital transformation and allocate resources to support it.
Organizational culture shift:
Encouraging a data-driven mindset and embracing change within the marketing team.
Employee training:
Equipping marketing staff with the necessary digital skills and knowledge to execute the strategy effectively.
What is a Digital Transformation in Marketing?
A digital transformation in marketing refers to the shift from digital complacency to the active pursuit of digital excellence
The 4C’s of Digital
Marketing is a customer-centric framework that focuses on understanding the
evolving needs of consumers in the digital era. The 4C’s model shifts the
traditional 4P's (Product, Price, Place, Promotion) of marketing to focus more
on the customer’s perspective and experience.
The 4C’s of Digital
Marketing are:
1. Customer (instead of
Product)
Focus: The customer is
at the heart of digital marketing. Instead of simply thinking about what
product to sell, marketers need to understand the needs, wants, and pain points
of the customer.
Why It Matters: In the
digital age, customers expect personalized experiences. They want solutions
that meet their specific needs, and they have more control over the buying
process. Understanding customer behavior, preferences, and intent is critical.
Examples:
Amazon uses customer
data and behavior to personalize product recommendations.
Netflix provides
tailored movie and TV show suggestions based on past viewing preferences.
Actionable Insights:
Use customer data and
insights to create personalized experiences.
Segmentation and
targeting are key, whether it's based on demographics, interests, or buying
history.
2. Cost (instead of
Price)
Focus: "Cost"
in the 4C’s model focuses on the total cost that a customer is willing to pay,
not just the price of the product. This includes considerations of time,
effort, and other intangible factors in the buying decision.
Why It Matters:
Customers want value for their money, and with easy access to information, they
compare prices, services, and alternatives across the digital landscape.
Examples:
Spotify offers both free
and premium subscription models, giving customers a choice based on how much
they’re willing to "pay" in terms of convenience, ads, and features.
Airbnb offers a variety
of options at different price points, with the "cost" to the customer
extending to the overall convenience of the booking process and property
selection.
Actionable Insights:
Offer flexible pricing
models, discounts, and rewards for loyalty.
Consider the total
customer experience cost, including the ease of purchase, product delivery,
customer service, etc.
3. Convenience (instead
of Place)
Focus: This C focuses on
convenience for the customer, especially in how easily they can access your
products and services. In the digital space, it's essential to make it simple
for customers to find, purchase, and interact with your brand, no matter where
they are.
Why It Matters: With the
rise of e-commerce, mobile shopping, and digital services, customers expect a
seamless, convenient experience across all channels (web, mobile, in-store,
social media).
Examples:
Apple’s website and app
provide easy access to product information, quick purchases, and efficient
customer service.
Uber makes booking a
ride convenient through its mobile app, which eliminates the need for calling
or hailing a cab.
Actionable Insights:
Invest in a
mobile-friendly website or app.
Use omnichannel
strategies to create a consistent experience across all platforms.
Streamline the checkout
process to minimize friction (e.g., one-click payment, easy form filling,
etc.).
4. Communication
(instead of Promotion)
Focus: Communication is
a two-way interaction between the brand and the customer. Unlike traditional
promotion, where businesses push messages to customers, digital marketing
allows for ongoing, interactive communication with customers.
Why It Matters: Digital
platforms give brands the ability to engage with their audience through social
media, email, reviews, and more. Building relationships and trust is key, as
customers expect brands to respond and engage.
Examples:
Nike uses social media
to not only promote products but also to engage with customers, celebrate
community events, and share customer stories.
Zappos has built a
reputation for exceptional customer service by fostering direct communication
with customers through social media, email, and phone.
Actionable Insights:
Leverage social media
for real-time communication and customer service.
Create content that
invites feedback and discussion.
Implement chatbots for
instant communication and personalized responses.
How the 4C’s of Digital
Marketing Work Together
The 4C’s framework is
centered around delivering a better customer experience and understanding the
shifts in consumer behavior in the digital world. By shifting focus from a
company-centered view (like the 4Ps) to a customer-centered approach,
businesses can:
Develop deeper insights
into customer behavior, preferences, and pain points.
Adapt pricing and
promotional strategies to suit customer expectations.
Ensure convenience and
seamless access to products and services across digital channels.
Foster two-way
communication to build trust, improve customer satisfaction, and create
long-term relationships.
Example of the 4C’s in
Action:
Let’s say you run an
e-commerce store selling fitness equipment.
Customer: You use
customer surveys, analytics, and social media engagement to identify that your
target audience is primarily young professionals aged 25-40 who want convenient
and effective home workout solutions.
Cost: Based on customer
feedback, you offer various pricing tiers: an entry-level package for
beginners, a premium set for fitness enthusiasts, and financing options for
high-ticket items.
Convenience: You offer a
mobile-friendly website with a one-click checkout process, fast delivery
options, and customer support available via chat and email. You also provide
product bundles for a seamless experience (e.g., dumbbells, resistance bands,
and yoga mats).
Communication: You
engage with your customers through regular email newsletters with fitness tips,
promotions, and personalized product recommendations. You actively reply to
customer queries on social media platforms and ask for feedback after
purchases, creating a sense of community.
Why the 4C’s Matter in
Digital Marketing
Customer Centricity: The
4C's ensure that your marketing strategy is customer-driven and focused on
delivering value.
Greater Engagement:
Shifting from a one-way promotional approach to interactive communication
increases customer engagement and loyalty.
Data-Driven: The model
encourages using data to understand customer needs, preferences, and behaviors,
which informs better decision-making and personalized strategies.
Flexibility: The 4C’s
are adaptable to various digital marketing platforms and business models,
whether you’re a B2C or B2B business.
Conclusion
The 4C’s of Digital
Marketing (Customer, Cost, Convenience, and Communication) help businesses
create a more holistic, customer-centric digital marketing strategy that aligns
with today’s digitally empowered consumers. By focusing on these areas, brands
can enhance customer satisfaction, improve conversion rates, and build
long-term, loyal relationships.
a) PPT - Project -1
b) Create soical media calender on Google PPT
c) Create different media (Reel/ shorts/ Video / Still / Infographics / Chart / Table and publish on different social media platforms using CANVA or any other software.
d) update your blog with 5 post (minimum) for self branding.
What is Social Media Marketing?
Social media marketing (SMM) is the practice of using social media platforms to connect with your audience to build your brand, increase sales, and drive website traffic. This involves 1 creating and sharing valuable content on social media, engaging with your followers, and running social media advertising campaigns.
Key Elements of Social Media Marketing
- Content Creation: Developing and sharing engaging content (text, images, videos) that resonates with your target audience.
- Community Building: Fostering a community around your brand by interacting with followers, responding to comments, and encouraging discussions.
- Social Media Advertising: Utilizing paid advertising options on social media platforms to reach a wider audience and target specific demographics.
- Analytics and Tracking: Monitoring social media performance using analytics tools to measure the effectiveness of campaigns and make data-driven decisions.
Facts and Figures
- Global Social Media Users: As of 2024, there are over 4.95 billion active social media users worldwide, representing nearly 61% of the global population. (Source: DataReportal)
- Time Spent on Social Media: On average, people spend nearly 2.5 hours per day on social media platforms. (Source: DataReportal)
- Social Media for Business: Over 90% of marketers say social media is important to their business. (Source: HubSpot)
- Social Media ROI: 89% of marketers report that their social media marketing efforts have increased exposure for their business. (Source: Sprout Social Index)
Examples of Effective Social Media Marketing
Nike: Nike excels at creating visually appealing content on Instagram that showcases its products and promotes an active lifestyle. They also leverage influencer marketing to reach a wider audience.
Wendy's: Wendy's is known for its witty and humorous Twitter presence, engaging with followers and even roasting competitors. This has helped them build a strong brand personality and attract a younger audience.
Wendy's Twitter interaction
Dove: Dove's "Real Beauty" campaign, launched on social media, challenged traditional beauty standards and promoted body positivity. This campaign resonated strongly with audiences and generated significant media buzz.
Dove Real Beauty campaign on social media
Benefits of Social Media Marketing
- Increased Brand Awareness: Social media provides a platform to reach a vast audience and increase visibility for your brand.
- Improved Website Traffic: Sharing content on social media can drive traffic to your website, increasing the chances of conversions.
- Enhanced Customer Engagement: Social media allows for direct interaction with customers, building relationships and fostering loyalty.
- Cost-Effective Marketing: Compared to traditional advertising, social media marketing can be a more budget-friendly option, especially with targeted advertising.
- Valuable Insights: Social media analytics provide valuable data about your audience, their preferences, and their behavior, helping you refine your marketing strategies.
Tips for Successful Social Media Marketing
- Define Your Goals: Determine what you want to achieve with social media marketing (e.g., brand awareness, lead generation, sales).
- Know Your Audience: Understand your target audience's demographics, interests, and online behavior.
- Choose the Right Platforms: Focus on the social media platforms where your target audience is most active.
- Create High-Quality Content: Share valuable and engaging content that resonates with your audience.
- Be Consistent: Post regularly and maintain a consistent brand voice across all platforms.
- Engage with Your Followers: Respond to comments and messages, and participate in relevant conversations.
- Track Your Results: Monitor your social media performance using analytics tools and make data-driven decisions.
https://rebeccacoleman.ca/2016/11/04/social-media/creating-social-media-marketing-plan-infographic
Social media marketing is a powerful tool for businesses of all sizes. By creating valuable content, engaging with followers, and utilizing analytics, you can leverage social media to build your brand, increase sales, and achieve your marketing goals.
Key points about social media marketing :
- Stay up-to-date with the latest trends and algorithm changes on social media.
- Be authentic and genuine in your interactions with your audience.
- Don't be afraid to experiment and try new things.
- Have fun and enjoy the process!
- What do you want to achieve?
- This is the foundational question.
- Are you aiming for brand awareness, lead generation, website traffic, direct sales, or customer service improvements?
- Your objectives should be SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound).
- Reach: How many people see your content.
- Engagement: Likes, comments, shares, clicks.
- Website traffic: Number of visitors driven from social media.
- Lead generation: Number of leads captured through social media forms or landing pages.
- Conversion rate: Percentage of leads that convert into customers.
- Brand mentions: Number of times your brand is mentioned.
- Sentiment: Positive, negative, or neutral mentions of your brand.
- Who are they? Demographics (age, gender, location, income, education), psychographics (interests, values, lifestyle), and online behavior.
- Where do they hang out? Which social media platforms are they most active on? Don't spread yourself too thin. Focus on the platforms where your audience is.
- What are their pain points? What problems do they have that your product or service solves?
- What kind of content do they like? What resonates with them? Do they prefer videos, images, text, infographics, live streams, or a combination?
- Match your audience to the platform. LinkedIn is great for B2B, Instagram for visual content and younger audiences, Facebook for broad reach, Twitter for news and real-time updates, TikTok for short-form video and Gen Z, etc.
- Consider platform strengths. Each platform has its own unique features and best practices.
- Content Pillars: Define 3-5 core themes related to your brand and audience interests. This creates consistency and focus.
- Content Calendar: Plan your content in advance. A calendar helps you stay organized and ensures a regular posting schedule.
- Content Mix: Vary your content types to keep things interesting.
- Educational: How-to guides, tutorials, tips and tricks.
- Entertaining: Humorous content, behind-the-scenes glimpses, user-generated content.
- Promotional: Product announcements, special offers, contests.
- Inspirational: Stories, quotes, testimonials.
- Interactive: Polls, Q&As, quizzes.
- Visual Content is King: High-quality images and videos are essential for grabbing attention.
- Storytelling: Connect with your audience on an emotional level through compelling stories.
User-Generated Content (UGC): Encourage your audience to create content about your brand. It builds trust and authenticity.
- Respond promptly and professionally. Address comments, questions, and concerns.
- Start conversations. Ask questions, run polls, and encourage discussions.
- Run contests and giveaways. This is a great way to increase engagement and grow your following.
- Collaborate with influencers. Partner with relevant influencers to reach a wider audience.
- Monitor brand mentions. Track what people are saying about your brand online.
- Targeted campaigns. Use platform targeting options to reach specific demographics, interests, and behaviors.
- Retargeting. Show ads to people who have previously interacted with your website or social media pages.
- A/B testing. Experiment with different ad creatives and targeting options to optimize your campaigns.
- Budget allocation. Allocate your advertising budget strategically across different platforms and campaigns.
- Track your KPIs. Regularly monitor your social media performance using platform analytics tools and third-party solutions.
- Analyze your data. Identify what's working and what's not.
- Adjust your strategy. Based on your data, refine your content, engagement, and advertising strategies.
- Regular reporting. Create reports to track progress and demonstrate the ROI of your social media efforts.
8. Staying Up-to-Date:
- Social media is constantly evolving. New platforms, features, and trends emerge regularly.
- Follow industry blogs and experts. Stay informed about the latest best practices.
- Experiment with new features. Don't be afraid to try new things.
- Objective: Increase brand awareness and drive foot traffic to the coffee shop.
- Target Audience: Young adults (18-35) in the local area, interested in coffee, cafes, and local events.
- Platforms: Instagram, Facebook, TikTok.
- Content Pillars: Coffee culture, local community, behind-the-scenes, special offers.
- Content Examples:
- Instagram: High-quality photos of coffee, latte art, food, and the cafe interior. Stories featuring daily specials, customer spotlights, and behind-the-scenes glimpses.
- Facebook: Posts about local events, community partnerships, and customer reviews. Run contests and giveaways.
- TikTok: Short, engaging videos showcasing coffee preparation, cafe ambiance, and fun challenges.
- Engagement: Respond to comments and messages, run polls and Q&As, collaborate with local influencers.
- Advertising: Targeted ads on Instagram and Facebook to reach the local audience.
- Analytics: Track followers, engagement, website traffic, and foot traffic to the cafe.
- By following these strategies and adapting them to your specific needs, you can create a successful social media presence that drives results for your business. Remember that consistency, creativity, and a data-driven approach are key to success.
Social media platforms have become integral to modern communication, networking, and content sharing. Here’s an overview of some of the most popular platforms, including Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, LinkedIn, Snapchat, and mobile-related social media experiences:1. FacebookLaunch Year: 2004Overview: Facebook is one of the largest social networking sites globally, allowing users to create personal profiles, connect with friends, share posts, photos, and videos, and join groups based on interests. It also includes features like Marketplace (for buying/selling items), Events, and Facebook Live (for live streaming).Target Audience: Broad demographic reach, used by individuals, businesses, and organizations for social interaction, marketing, and community building.
2. Instagram
Launch Year: 2010Overview: Instagram initially focused on photo sharing and has since expanded to include Stories (temporary posts), Reels (short video content), IGTV (longer video content), and shopping features. It emphasizes visual content, making it a platform for influencers,
3. TwitterLaunch Year: 2006Overview: Twitter is a microblogging platform where users can post and interact through "tweets" (short messages limited to 280 characters). It facilitates real-time news updates, discussions, and trends, making it popular among journalists, public figures, and businesses.Target Audience: Users seeking real-time news, opinions, and engagement on current events; used frequently by politicians, celebrities, and thought leaders.
4. LinkedInOverview: LinkedIn is a professional networking platform designed for job seekers, professionals, and businesses. Users can create profiles, connect with colleagues, share industry-related content, apply for jobs, and showcase their professional experiences and skills.Target Audience: Working professionals, recruiters, and businesses across all industries looking to network, hire, or build their brand presence.
5. SnapchatLaunch Year: 2011
Overview: Snapchat is known for its unique features like disappearing messages and a strong emphasis on ephemeral content. Users can send photos and videos that vanish after being viewed, as well as engage in stories that last 24 hours. The platform has expanded to include features like filters, lenses, and discovery content.Target Audience: Primarily younger audiences, particularly Gen Z, who prefer casual and instantaneous sharing of multimedia content.
6. Mobile Social MediaOverview: Many social media platforms have robust mobile applications, allowing users to engage with content seamlessly on smartphones and tablets. Mobile social media focuses on instant connectivity, instant sharing, and location-based features.
Key Features:Notifications & Alerts: Users receive instant updates about interactions.Location-Based Services: Many platforms incorporate geolocation features for sharing experiences or finding local events.
Mobile Shopping Integration: Platforms like Instagram and Facebook enable users to purchase products directly through their mobile apps.
ConclusionEach social media platform has its unique attributes, audiences, and purposes. Facebook and LinkedIn cater to social and professional networking, respectively, whereas Instagram and Snapchat focus heavily on visual and ephemeral content. Twitter remains a go-to for real-time information and updates. Understanding the nuances of each platform can help users and businesses leverage them effectively for communication, branding, and community engagement.
1. FacebookProfile Picture: 180 x 180 pxCover Photo: 820 x 312 pxPost Image: 1200 x 630 pxStory: 1080 x 1920 px2. InstagramProfile Picture: 110 x 110 pxPost Image: 1080 x 1080 px (Square) or 1080 x 1350 px (Portrait)Story: 1080 x 1920 pxReels: 1080 x 1920 px3. TwitterProfile Picture: 400 x 400 pxHeader Image: 1500 x 500 pxPost Image: 1200 x 675 pxPinned Post Image: 1200 x 675 px4. LinkedInProfile Picture: 400 x 400 pxCover Photo: 1584 x 396 pxPost Image: 1200 x 1200 pxStory: 1080 x 1920 px5. YouTubeProfile Picture: 800 x 800 pxChannel Art: 2560 x 1440 px (with safe area 1546 x 423 px)Thumbnail: 1280 x 720 pxPost Image (YouTube Community): 1200 x 1200 px
6. Pinterest
Profile Picture: 165 x 165 pxPin Image: 1000 x 1500 pxBoard Cover Image: 222 x 150 px
Content planning and strategy in social media marketing refer to the process of creating a structured approach to producing, publishing, and managing content across social media platforms. This process is vital for ensuring that the content aligns with business goals, resonates with the target audience, and effectively engages users. Here's a breakdown of what content planning and strategy typically involve:
1. Understanding Objectives:
Goal Setting: Define clear objectives for your social media efforts (e.g., brand awareness, user engagement, lead generation, driving traffic to a website).
KPIs: Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure success, such as engagement rates, follower growth, conversion rates, and website traffic from social channels.
2. Audience Research:
Target Audience: Identify and understand your target audience, including demographics, interests, behaviors, and pain points.
Personas: Create buyer personas to visualize and empathize with your audience, ensuring that content is tailored to their needs and preferences.
3. Content Themes and Topics:
Content Pillars: Develop core themes or topics that will guide your content creation, ensuring consistency and relevance.
Trends and Challenges: Stay updated on industry trends, challenges, and news that are relevant to your audience to inform content topics.
4. Content Calendar:
Scheduling: Create a content calendar that outlines what content will be published, when, and on which platforms. This helps streamline the workflow and ensures a consistent posting schedule.
Content Types: Include various content formats (e.g., images, videos, blogs, infographics, polls) to keep the audience engaged.
5. Content Creation:
Production: Develop high-quality and visually appealing social media content that aligns with brand voice and messaging.
Collaboration: Involve relevant team members, such as designers, copywriters, and social media managers, in the content creation process.
6. Publishing and Distribution:
Platform Specificity: Tailor content for each social media platform (e.g., Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, LinkedIn) based on its unique audience and features.
Optimal Timing: Determine the best times to publish content for maximum visibility and engagement based on audience behavior and analytics.
7. Engagement and Community Management:
Interaction: Monitor social media channels actively, responding to comments, messages, and interactions to build relationships with the audience.
User-Generated Content: Encourage and curate content created by users that aligns with your brand, fostering community and engagement.
8. Analytics and Evaluation:
Performance Tracking: Regularly analyze the performance of social media content against your KPIs.
Feedback Loop: Use insights gained from analytics to refine strategies, adjust content types, and optimize future campaigns.
9. Adjustment and Innovation:
Iterative Process: Content strategy should be flexible, allowing for adjustments based on feedback, analytics, and changing market trends.
Experimentation: Test new content types, messaging strategies, and advertisement options to discover what resonates best with the audience.
Conclusion
A well-defined content planning and strategy in social media marketing enables brands to connect with their audience, deliver valuable content, and achieve marketing goals effectively. It requires ongoing evaluation and refinement to remain relevant in an ever-changing digital landscape.
Facts and Figures
Importance of Content in Marketing:
93% of Marketers: According to the Content Marketing Institute, 93% of marketers use content marketing to reach their customers.
Inbound Marketing Growth: HubSpot reports that inbound marketing (which heavily relies on content) generates 54% more leads than traditional marketing.
Engagement Statistics:
Higher Engagement: Content marketing generates three times as many leads as traditional outbound marketing and costs 62% less (source: Demand Metric).Social Media Visuals: Posts with images receive 650% higher engagement than text-only posts (source: HubSpot).
Content Consumption Trends:
Video Dominance: By 2022, online videos accounted for more than 82% of all consumer internet traffic, according to Cisco. This highlights the growing importance of incorporating video into content strategies.
Blogging Stats: Websites that blog have 434% more indexed pages and get 97% more backlinks than those without blogs (source: HubSpot).
SEO and Content:
Organic Search Traffic: Businesses that prioritize blogging are 13 times more likely to see positive ROI (source: HubSpot).
SEO Impact: Content marketing can lead to 14.6% conversion rates, as compared to only 1.7% for traditional outbound methods (source: HubSpot).
Content Formats:
Ebooks and Whitepapers: 78% of people prefer to receive information in a format that suits their needs, with ebooks and whitepapers being among the most popular (source: HubSpot).
Webinars: According to ON24, 73% of B2B marketers cite webinars as the best way to
generate quality leads.
Content = KING = Content is soul of Digital Marketing 
Examples of Successful Content Marketing Strategies
HubSpot:
Strategy: HubSpot is a leading example of a company that utilizes inbound marketing through its blog and educational resources. They provide valuable content in the form of guides, eBooks, and webinars.
Results: HubSpot has grown significantly, generating more leads and establishing itself as a thought leader in the marketing automation space.
Coca-Cola:
Strategy: Coca-Cola's "Content 2020" initiative aimed to emphasize branded storytelling. Instead of traditional advertising, the brand focuses on creating engaging content that resonates with consumers' emotions.
Results: Their "Share a Coke" campaign allowed consumers to buy bottles with their names, significantly increasing engagement and sales.
Airbnb:
Strategy: Airbnb’s “Airbnb Magazine” and the blog feature authentic stories and experiences from hosts and travelers. They prioritize user-generated content to create community and trust.
Results: This content strategy not only helped build brand loyalty but also encouraged more users to engage with the platform.
Buffer:
Strategy: Buffer utilizes a blog that shares social media strategies, industry updates, and case studies. They also practice transparency by sharing their company's growth metrics publicly.
Results: This has helped establish Buffer as a trusted source in the social media management space and built a loyal community around the brand.
Red Bull:
Strategy: Red Bull has mastered content marketing by positioning itself in extreme sports and adventure, creating engaging videos and documentaries that embody their brand ethos.
Results: Red Bull's YouTube channel has hundreds of millions of views, and they have successfully built an entire media empire around the brand.
Conclusion
Content planning, strategy, and marketing are critical components of a successful digital marketing approach. The evolution of consumption patterns, along with the statistics noted above, strongly supports the need for brands to invest in thoughtful content creation strategies that engage audiences and drive results. As evident from successful case studies, when executed well, content marketing can lead to significant business growth and brand loyalty.
Unit -3
a) Create buyer's persona using Excel
b) Keyword research
c) Website Audit
d)Configure Google ads
Follow this step-by-step guide to configuring ads on Google Ads, along with relevant images to help learners implement it easily.
Step 1: Sign in to Google Ads
Go to Google Ads.
Click Sign in or Get started if you don’t have an account.
Follow the setup prompts, including entering your billing information.
Step 2: Create a New Campaign
Click on New Campaign in the dashboard.
Choose your campaign goal:
Sales – Drive online or in-store sales.
Leads – Get sign-ups or form submissions.
Website Traffic – Increase visits to your website.
App Promotion – Promote a mobile app.
Brand Awareness – Increase reach and brand visibility.
Step 3: Select Campaign Type
Choose the type of ad campaign:
Search Ads – Show text ads in Google Search results.
Display Ads – Appear on websites in Google’s network.
Video Ads – YouTube video promotions.
Shopping Ads – Promote products from an online store.
Performance Max – Uses AI for multiple placements.
Step 4: Configure Campaign Settings
Name your campaign (e.g., "Summer Sale 2025").
Select Networks – Google Search, Display Network, or YouTube.
Set Start & End Dates (if needed).
Choose Target Locations & Languages – Define where your ad should be shown.
Step 5: Set Up Budget & Bidding
Choose your daily budget (e.g., $10/day).
Select a bidding strategy:
Maximize clicks – Get as many clicks as possible.
Target CPA (Cost per Acquisition) – Optimize for conversions.
Target ROAS (Return on Ad Spend) – Optimize for revenue.
Step 6: Define Audience & Targeting
Keywords Selection – Use the Keyword Planner tool to find relevant keywords.
Demographics – Target users based on age, gender, income, etc.
Interests & Behaviors – Show ads to users based on their online activity.
Step 7: Create Your Ad
Enter Headline (max 30 characters) – e.g., "50% Off Summer Sale!"
Enter Descriptions (max 90 characters) – e.g., "Limited-time offer. Shop Now!"
Add Display URL – e.g., "www.example.com/sale".
Upload Ad Assets (for Display/Video Ads) – Images, videos, or banners.
Step 8: Review & Launch
Double-check your settings.
Click Publish to launch your campaign.
Monitor performance in the Google Ads Dashboard.
Unit -4
a) Create a sample analytics report (real or mock data) using Google Analytics Configuration for Interpreting Google Analytics for a Website.
b) Revision Tour
c) Quiz Time
d) Case Studies


















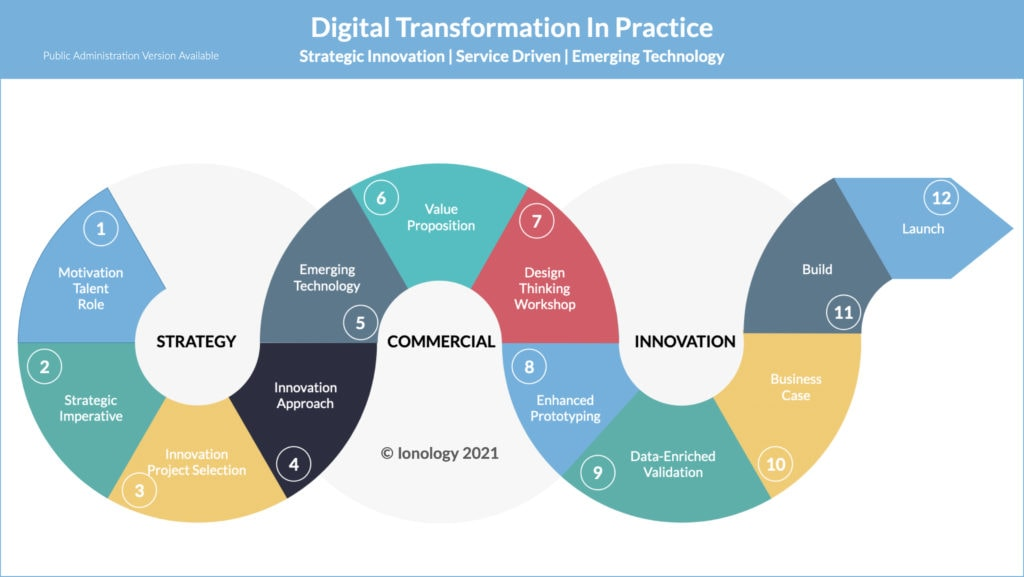






























No comments:
Post a Comment
If you have any query or doubt, please let me know. I will try my level best to resolve the same at earliest.